
Enterprise Cloud Definition, Business Benefits and Key Solutions
In today’s fast-paced business world, staying ahead of the competition requires innovation, agility, and the ability to harness the power of cutting-edge technology.
Enter the enterprise cloud – an innovative approach to developing, connecting, and hosting software applications that greatly improves business efficiency and future expansion capabilities.
In this article, we’ll set out to demystify the enterprise cloud, explore its myriad benefits, and highlight key solutions. Get ready to take your business to the cloud, where the possibilities are virtually endless!
Contents
- What is enterprise cloud? Definition
- Why use an enterprise cloud? The six key benefits
- Key statistics on enterprise cloud for 2025
- Who uses an enterprise cloud?
- What are the different types of enterprise cloud architecture?
- Popular examples of cloud solutions
- Enterprise cloud strategy – How to conduct a seamless cloud adoption
- Best practices for enterprise cloud transition
- FAQ
What is enterprise cloud? Definition
Enterprise Cloud is a comprehensive and tailored cloud computing solution designed to meet the needs of large organizations and enterprises. It represents a cohesive IT operational cloud environment that integrates private, public and distributed clouds and provides a centralized control hub to manage infrastructure and applications across all cloud types.
Unlike traditional cloud services designed for individual users or small businesses, the Enterprise Cloud leverages the full potential of cloud technologies and cloud infrastructure to deliver a scalable, secure, high-performance, and agile experience for both management and consumers.
As a result, organizations can streamline operations, optimize resources, and achieve remarkable efficiencies while maintaining heightened privacy and compliance standards. As a result, enterprise cloud platform solutions can be a real game changer for organizations across multiple industries.
Why use an enterprise cloud? The six key benefits
In today’s business landscape, the adoption of enterprise cloud solutions has become a game-changer for countless organizations worldwide. Let’s take a closer look at the six compelling benefits that enterprise cloud solutions offer modern businesses.
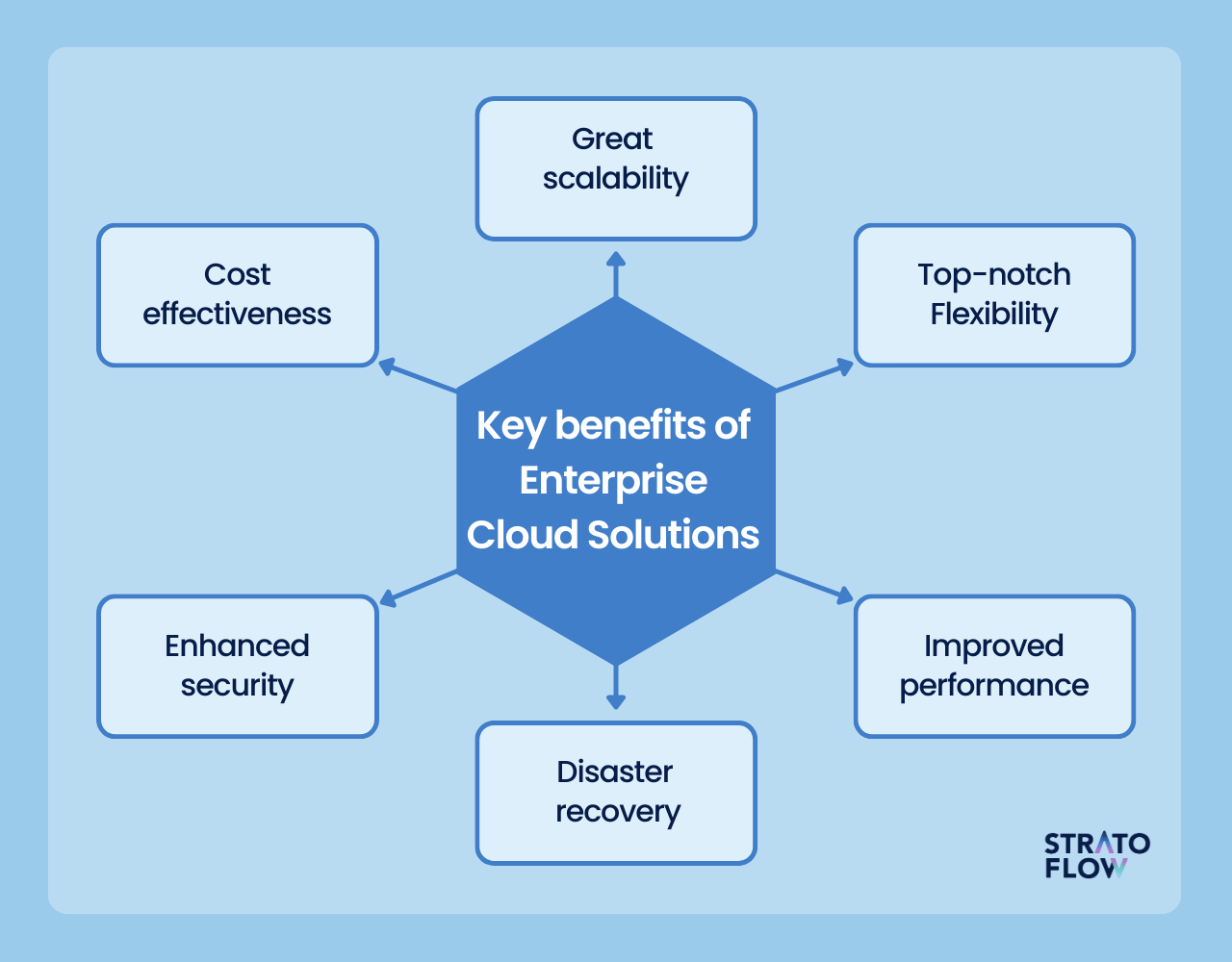
Cost Effectiveness
Above all else thanks to moving to the cloud large enterprises can gain significant cost advantages. With cloud services, they can move from the traditional capital expenditure model to a more flexible pay-as-you-go approach. This allows companies to pay only for the cloud computing resources they use, avoiding the burden of up-front investments in hardware and data centers.
Scalability
Cloud computing also offers unparalleled scalability, enabling large enterprises to seamlessly meet fluctuating demand.
Unlike on-premises solutions, where scaling up can be time-consuming and costly, cloud environments allow organizations to quickly expand resources to meet surges in user traffic or business growth. Conversely, they can scale down during periods of lower demand, avoiding unnecessary costs. This cloud computing scalability enables businesses to remain agile and responsive in a dynamic marketplace.
Flexibility
The inherent flexibility of the cloud enables large enterprises to innovate and experiment faster. Cloud platforms facilitate rapid application deployment and different types of software testing, reducing time to market for new products and services.
Software developers and teams can access a wide range of cloud-based tools and services, fostering a culture of innovation and iteration. This flexibility also facilitates seamless integration with other systems, allowing businesses to adapt and evolve as needs change.
Improved performance
Cloud computing is a powerful tool that enables organizations to achieve new levels of software performance.
Reputable cloud providers offer sophisticated infrastructures that distribute computing resources across multiple data centers, minimizing latency and ensuring consistently high performance. Keep in mind that to realize the full performance potential of cloud architectures, the underlying software architecture must also meet the highest standards.
By taking smart approaches to software development, such as multi-tenant database architecture, selecting the right tech stack for the project, and writing code according to the latest software development best practices, organizations moving their services to the cloud can deliver faster and more responsive applications, resulting in an improved user experience and customer satisfaction.
[Read more: Legacy Software Systems: How to Live with Aging Software Architecture?]
Enhanced security
Contrary to common misconceptions, a well-designed enterprise cloud solution can often significantly improve data security for large organizations compared to on-premises systems.
First and foremost, enterprise cloud solutions use advanced encryption algorithms to protect data during transmission and in storage. This ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains encrypted and unreadable, providing an extra layer of protection against potential breaches. To further strengthen access controls, cloud providers also implement multi-factor authentication, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to sensitive resources.
In addition, cloud providers are required to adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, depending on the type of data and industries they serve. All of this ensures world-class data protection and redundancy.
Disaster recovery
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery capabilities that protect large enterprises from data loss and service interruption.
You don’t have to worry about setting up complicated RAID arrays in your on-premises data center or backup data storage because cloud providers implement automated backup and recovery solutions that ensure critical data is replicated across multiple servers in different geographic regions. In the event of a hardware failure or unexpected incident, businesses can quickly restore operations and minimize downtime.
Key statistics on enterprise cloud for 2025
- According to Gartner, worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to grow 20.4% to total $678.8 billion in 2025, up from $563.6 billion in 2023.
- The fastest-growing segment is infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), which is expected to increase by 26.6% in 2025.
- The rise of industry cloud platforms, which are projected to be used by more than 70% of enterprises by 2027
- Gartner has also identified 10 strategic technology trends for 2025, many of which are related to cloud computing. Some of these trends include AI Trust, Risk and Security Management (AI TRiSM), Industry Cloud Platforms, Sustainable Technology and Democratized Generative AI.
- Gartner also made some predictions for 2025 and beyond, such as the rise of GenAI, which is the use of generative AI to create and collaborate with humans. GenAI will impact personal and professional development, business performance, and national power.
- Four trends are shaping the future of the public cloud: cloud ubiquity, regional cloud ecosystems, sustainability and carbon intelligent cloud, and automated programmable infrastructure. These trends will enable cloud providers to deliver greater value, differentiation and innovation to their customers.
- Edge computing and native clouds are two complementary trends that will enable faster and more scalable cloud applications. Edge computing brings computing closer to the data source, while native clouds leverage cloud-native technologies such as containers and microservices.
Who uses an enterprise cloud?
The benefits of cloud-based software solutions have not gone unnoticed by major organizations in various industries. From cutting-edge advances in healthcare to seamless e-commerce experiences, cloud computing technology has transformed many industries, driving innovation, efficiency, and growth.
Here are six key examples of industries that have successfully leveraged enterprise cloud solutions in their operations:
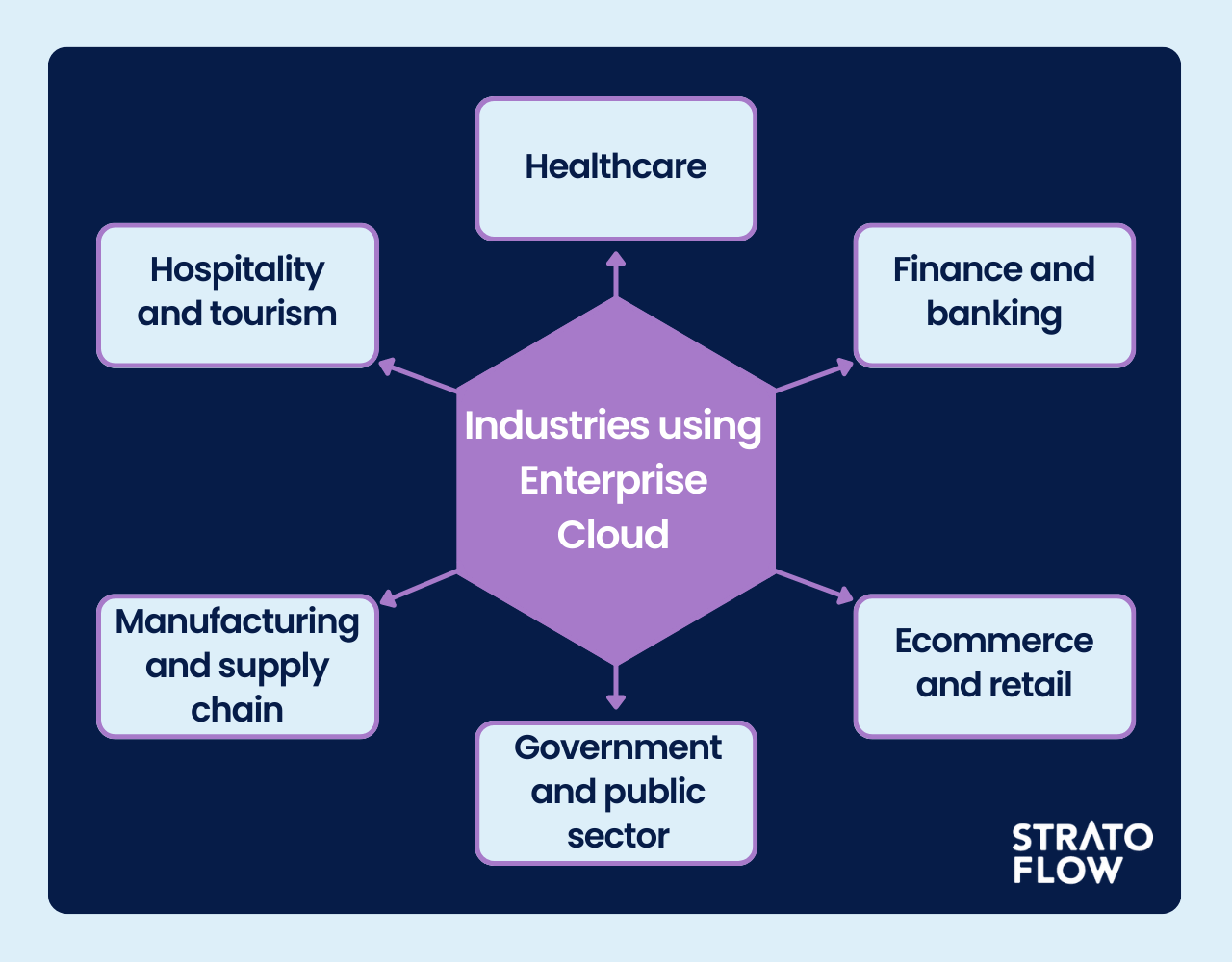
Healthcare
Cloud services can have a profound impact on the healthcare industry, revolutionizing the way healthcare providers deliver services, manage patient data, and collaborate across the healthcare ecosystem.
Cloud-based electronic health record (EHR) systems enable seamless data sharing and interoperability across healthcare facilities. Providers can securely access patient information in real time, leading to more informed clinical decisions, reduced medical errors, and improved patient outcomes. What’s more, the increased data security offered by cloud-based platforms is a major benefit for healthcare companies that store incredibly sensitive customer data.
On a more innovative note, cloud-based IoT platforms facilitate the integration of wearable devices and remote monitoring tools. This allows healthcare providers to collect and analyze patient data in real time, enabling proactive care management and early intervention.
Finance and Banking
Fintech and banking services are another area where cloud services can have a profound impact.
The key benefit of the cloud approach for the fintech industry is cost efficiency. By moving away from on-premises data centers and hardware, they can leverage a pay-as-you-go model, reducing capital expenditures and optimizing IT spending. Cloud solutions also offer on-demand cloud scalability, allowing organizations to expand or contract resources as needed, ensuring consistent performance and uninterrupted service availability.
Finally, some cloud-based analytics platforms enable financial institutions to derive valuable insights from vast amounts of financial data using advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to detect patterns, identify fraud, and provide personalized financial services to customers.
[Read also: What Are Large Language Models: Definition + Best Examples]
E-commerce and Retail
By now, we should be seeing a pattern emerge – industries that deal with large amounts of data benefit the most from using cloud services. This means that e-commerce should be another business that takes advantage of the cloud. And it is.
For starters, enterprise cloud computing allows e-commerce and retail companies to quickly scale their operations to meet fluctuating demand. During peak shopping seasons or promotions, companies can easily scale resources to handle increased site traffic and transactions, ensuring a smooth customer experience.
Cloud enterprise software solutions also offer improved performance and reliability, which is critical for e-commerce sites. With built-in content delivery networks (CDNs), they enable reduced latency, ensuring fast page load times and minimizing the risk of downtime. E-commerce sites also benefit from standard cloud-related issues such as security, global accessibility, and cost optimization.
Government and Public Sector
The public sector also benefits greatly from the security, scalability, and adaptability of the cloud environment.
For these organizations, the cost of running and maintaining software systems is one of the most critical issues. With cloud computing services, government organizations can move from a capital expenditure model to an operating expenditure model, paying only for the resources they use. This cost optimization allows them to allocate budgets more efficiently and redirect savings to essential programs and services.
What’s more, cloud-based backup and disaster recovery services protect critical data and applications from potential disasters. Many valuable documents in the public sector need to be archived for years or even decades, so this added redundancy is critical for government organizations.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Cloud solutions also offer significant improvements to the manufacturing industry, greatly optimizing operations, streamlining processes, and driving innovation.
Cloud-based manufacturing execution systems (MES) and industrial IoT (IIoT) platforms enable manufacturers to collect real-time data from connected devices and sensors on the factory floor. This data visibility facilitates data-driven decision making, process optimization, and predictive maintenance, ultimately improving overall efficiency and productivity. In addition, the cloud can also enable companies to realize significant cost savings and improve flexibility and scalability.
Hospitality and Tourism
Last but not least, the travel and hospitality industry also benefits greatly from cloud solutions in one form or another.
Cloud-based reservation systems, booking engines, and inventory management systems provide real-time availability of rooms, flights, and travel packages. All of these travel systems ensure that travelers have access to up-to-date information and can conveniently book their travel arrangements, improving customer satisfaction.
What are the different types of enterprise cloud architecture?
By now, we know which companies are using enterprise cloud solutions and the benefits they bring. Now let’s take a closer look at these cloud systems, covering four main types and their key applications.
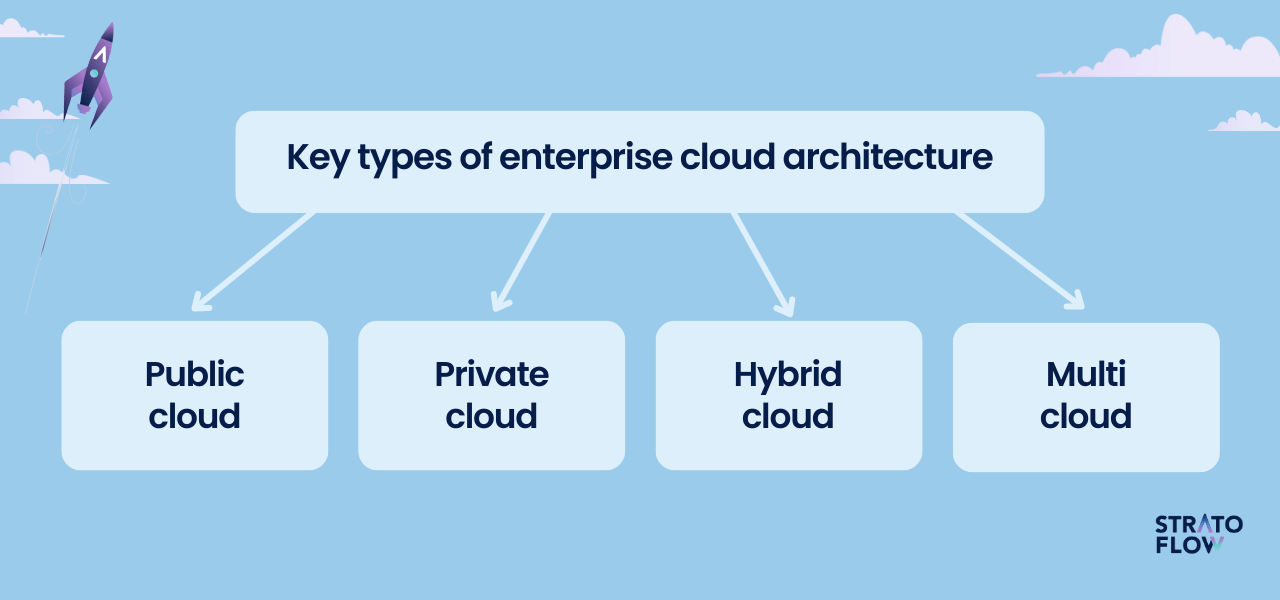
Public Cloud
Public cloud solutions are offered by large third-party providers and are available to the general public and to multiple organizations. By leveraging the vast resources of public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), businesses can access a wide range of services and applications on-demand, without the burdensome requirements of hardware maintenance or upfront capital investment. The public cloud approach is ideal for startups and smaller businesses seeking agility and flexibility while enjoying the benefits of economies of scale.
Private Cloud
At the other end of the spectrum is the private cloud, which is carefully tailored to meet stringent security and compliance requirements. Built exclusively for a single organization, private cloud platforms allow companies to maintain control over their sensitive data and configurations, while offering a level of customization and performance that public clouds may struggle to match.
Larger enterprises, particularly those in highly regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, often prefer the private cloud infrastructure approach to protect intellectual property and maintain data sovereignty.
Hybrid Cloud
Recognizing the potential synergies between private and public clouds, the hybrid cloud is emerging as a strategic fusion that brings together the best of both worlds.
This approach enables seamless portability of data and applications between on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services, allowing enterprises to enjoy the elasticity of public clouds for non-sensitive tasks while keeping sensitive data behind the secure boundaries of the private cloud. Hybrid clouds provide the adaptability sought by organizations with dynamic workloads and fluctuating resource requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Multi-cloud
Finally, the multi-cloud approach is taking center stage as diverse enterprises seek to embrace the diversity and redundancy of cloud ecosystems. In this innovative strategy, enterprises spread their workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing the risk of vendor lock-in and increasing resilience to outages. By cherry-picking the best services from different cloud providers, enterprises can optimize their cloud architecture, meet diverse user needs, and fine-tune cost management strategies.
Multi-cloud adoption is on the rise as enterprises seek to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage the strengths of different cloud providers. By leveraging distributed cloud and dividing workloads across multiple clouds, enterprises can improve reliability, redundancy, and system performance.
Popular examples of cloud solutions
There are a number of major cloud service providers on the market today. Each offers high-quality cloud hosting services, and the decision of which cloud provider to choose should boil down to specific offerings and project specifications. However, here are three of the most popular cloud computing service providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – AWS is one of the most popular and comprehensive cloud service providers, offering a wide range of services such as computing power, storage, databases, machine learning, analytics, and more.
- Microsoft Azure – Microsoft Azure provides a robust cloud computing platform with services for virtual machines, AI and machine learning, data analytics, IoT, and various other enterprise-grade solutions.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – GCP offers a suite of cloud services, including cloud computing, data storage, machine learning, data analytics, and application development tools, backed by Google’s global infrastructure.
[Read more: Top 10 Software Development Methodologies: How to Choose the Right One?]
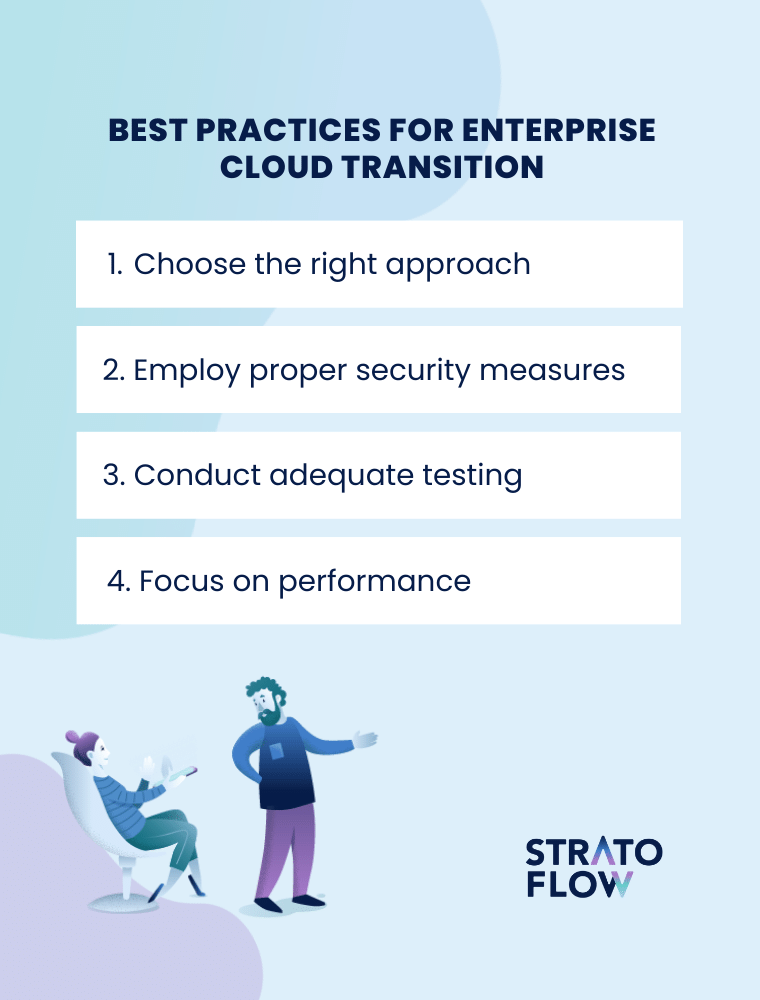
Enterprise cloud strategy – How to conduct a seamless cloud adoption
A successful enterprise cloud strategy is a harmonious symphony of tailored software solutions and powerful cloud service providers working seamlessly together for optimal performance and efficiency. Adapting the enterprise to a cloud-native world can be challenging. Fortunately, there are some best practices to follow to make the transition to the enterprise cloud a smoother process.
Best practices for enterprise cloud transition
Choose the right approach
The first area to consider when creating an enterprise cloud strategy is how to set up your cloud environment to meet your organization’s needs.
There are different ways to set up your enterprise cloud, for example, you can choose to containerize. Using solutions like Docker or Kubernetes provides a lightweight and scalable way to package applications with their dependencies, making them portable across different cloud environments.
There’s also a cloud-native architecture approach that’s been gaining attention in recent years. It refers to the practice of designing applications specifically for the cloud, using microservices, DevOps practices, and continuous system integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to improve scalability and resilience. We should also mention serverless architecture, which is a type of cloud-native approach in which organizations run software applications without managing servers. Cloud providers handle the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on code development.
Employ proper security measures
Because enterprise cloud systems handle vast amounts of sensitive data that is constantly being transferred between servers and users’ machines, security should be a top priority when developing a cloud migration strategy.
First and foremost, enforce strong access controls and authentication mechanisms. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive data and resources to authorized personnel.
There are also ways to strengthen enterprise cloud security while allowing team members to collaborate. By leveraging cloud-based chip design and cloud-enabled applications, teams can be confident that both the software and hardware going into the cloud meet enterprise-grade reliability, support, and security standards.
Conduct adequate testing
Another critical aspect of a solid enterprise cloud strategy is migrating your testing processes to the cloud. Testing in the cloud offers numerous benefits, including inherent support for different network setups and authentication methods, as well as overall cost efficiencies.
Thorough testing improves system reliability, security, and performance, reducing the risk of downtime or data breaches that could have significant financial and reputational consequences for the organization. Out of different types, performance testing might be the most important as it directly checks how stable, scalable and responsive a given piece of software is under a specific load. Having said that, validating software functionality and usability, testing also improves user satisfaction and increases confidence in the system’s capabilities, ultimately leading to better business outcomes and operational efficiency.
Focus on performance
Improving system performance has become a critical goal for businesses seeking a competitive edge. A high-performing cloud system delivers not only a seamless user experience, but also increased productivity, optimal resource utilization, and unmatched scalability.
Tweaking things like caching, content delivery, and resource allocation can greatly improve both physical and perceived user performance. Another important place to look for optimizations and better efficiency is in the databases, where you can improve database management, indexes, and data structures to reduce query response times. If you are looking for better resource utilization, look into multitenant database solutions. In a multitenant architecture, multiple clients or tenants share a single database instance, allowing for efficient use of hardware resources. By dynamically allocating resources based on demand, the multitenant cloud database system can effectively balance workloads and optimize performance during peak usage periods.
Having said that, building a high-performance cloud enterprise software solution is an incredibly complex task with so many intricacies and complexities that we could not even fit it into ten of these articles. In fact, we’ve barely scratched the surface of this complex and fascinating topic. In addition, every business and its data workload is different, requiring a customized solution to achieve the best results. As you embark on this journey, it is best to seek the help of a custom software development company that specializes in creating highly scalable, high-performance cloud software solutions.
[Read more: The Future of Software Engineering: Key Emerging Trends]
Related Posts
- How to Build an Inventory Management System: Key Steps and Tips
- How to Build a Document Management System: Alternative Approach
- Online Shopping Recommendations – Introducing Them to Your Business
- Amazon Product Recommendation System: How Does Amazon Algorithm Work?
- Movie Recommendation Systems: A Business Guide
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog post!
FAQ
What is a cloud definition?
A cloud refers to a network of remote servers hosted on the internet that store, manage, and process data and applications. Cloud computing allows users to access and utilize computing resources, such as storage, processing power, and software, on-demand over the internet without the need for physical hardware or infrastructure.
Why is called the cloud?
The cloud in cloud computing reflects the abstraction of underlying infrastructure, as users access services and data over the internet without needing to know the specific physical locations or details of the servers hosting those resources.
What is cloud-based enterprise application?
A cloud-based enterprise application refers to a software application or service that is hosted, managed, and accessed through the internet, rather than being installed and operated on local hardware or servers. These applications leverage cloud computing infrastructure to deliver scalable, flexible, and on-demand solutions to businesses and organizations.
What is the cloud technology?
Cloud technology refers to a collection of internet-based computing resources, services, and infrastructure that enable users to store, process, and access data and applications remotely over the internet.
What is the difference between cloud and enterprise cloud?
The term “cloud” encompasses a wide range of internet-based computing services accessible to the public cloud, while “enterprise cloud” refers to tailored solutions designed for large organizations with specific security and customization needs.
What is the largest enterprise cloud?
The largest enterprise cloud belongs to Amazon Web Services (AWS). With an extensive global infrastructure spanning data centers in numerous regions, AWS provides a vast array of services to businesses and organizations of all sizes.
What do enterprises use the cloud for?
Enterprises use the cloud for a wide range of purposes, leveraging its capabilities to enhance efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud computing allows businesses to store and access data remotely, host applications, and run various workloads without relying on physical on-premises infrastructure.
