
How to Start Real Estate Business in 2024
Considering diving into the world of real estate in 2024?
With the market’s ever-evolving dynamics and promising growth prospects, it’s an enticing venture for many. But where does one begin?
This article will guide you through the essential steps to launch a successful real estate business in the current landscape, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities ahead. Let’s embark on this exciting journey together.
Contents
- What is real estate?
- What is a real estate business?
- Types of real estate classifications
- How does real estate agency work?
- How much does it cost to own real estate business
- Business benefits of starting your own real estate company
- How to start a real estate business in 15 steps
- Understanding real estate industry
What is real estate?
Real estate, by definition, includes land and anything permanently attached to it, be it buildings, houses, or natural resources such as water and crops.
This is the definition that has been around in one form or another since the time of the Roman Empire.
In a business context, real estate revolves around the buying, selling, and renting of property with the primary focus on generating profit through strategic management and investment.
The real estate market is diverse, encompassing various sectors such as residential, commercial and industrial, each with its own characteristics and regulatory environment.

What is a real estate business?
As we’ve already mentioned, at its core, the real estate business involves activities related to developing, buying, selling, and leasing real estate with the goal of generating substantial returns on investment.
In reality, however, it’s much more complex than that.
In today’s global market, owning your own real estate business is not limited to property acquisition, but extends to property management, real estate development, brokerage, and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
Entrepreneurs in this domain leverage strategic planning, market analysis, and financial acumen to optimize the value of assets, ensuring profitability and sustainability amidst the fluctuating market dynamics.
Types of real estate classifications
No two real estate assets are alike.
They all vary in size, location, age, and materials used in construction.
That said, we can distinguish a few key types of real estate based on their primary use.
It’s pretty important to understand these classifications before deciding to start a real estate business.
Residential Real Estate
This includes both new construction and resale homes. The most common category is single-family homes, but it also includes:
- Condominiums: Individual units in a building with multiple units.
- Co-ops: Where the residents own shares of a corporation, which owns the building or development.
- Townhouses: Single-family homes that are placed side-by-side.
- Multi-family dwellings: Such as apartment buildings.
Commercial Real Estate
This category of real estate includes shopping centers, strip malls, medical and educational buildings, hotels, and offices. Apartment buildings are often considered commercial, even though they are used for residences, due to their mode of being an income-generating asset.
Industrial Real Estate
This category includes manufacturing buildings and property, as well as warehouses. The buildings can be used for research, production, storage, and distribution of goods.
Vacant Land
This includes vacant land, working farms, and ranches. The subcategories within vacant land include:
- Undeveloped: Land that is undeveloped.
- Early Development or Reuse: Includes demolished property or reclaimed land.
- Site Assembly: Merging and assembling of parcels of land.
Special Purpose
Last but not least, this broad category includes property that is appropriate for a specific use, like schools, churches, or cemeteries.
How does real estate agency work?
So how does the most popular types of real estate business, real estate agencies, conduct their operations?
that serve as a critical intermediary in the property market, facilitating transactions and providing specialized services to both buyers and sellers.
The operational framework of an agency in the real estate domain involves five key aspects:
- Client Representation: Agencies act on behalf of clients, providing specific services such as market analysis, negotiation support, and transaction oversight.
- Property Listing and Marketing: The agency manages property listings and employs strategic marketing tactics to maximize visibility and attract prospective buyers or tenants, aiming to secure advantageous transactions for clients.
- Negotiation and Transaction Management: Real estate agents engage in negotiation processes, advocating for favorable terms and prices for their clients. They oversee transactions from initiation to closure, ensuring adherence to legal and contractual obligations.
- Legal and Regulatory Adherence: Agencies ensure that all transactions comply with existing legal and regulatory standards.
- Revenue through Commissions: The primary revenue model for real estate agencies is commission-based, wherein real estate agents earn a predetermined percentage of the transaction value, ensuring that revenue is generated upon the successful completion of a transaction.
How much does it cost to own real estate business
As you might have assumed starting and running a real estate business involves various costs, and while the exact amount can vary based on location, market conditions, and individual choices. To be prepared what’s ahead here’s a breakdown based of what you might expect when running a real estate agency:
Educational Costs
- Pre-Licensing Courses: $300 – $600
- Real Estate Exam Prep: $50 – $125
- Post-Licensing: $50 – $450
Licensing and Association Fees
- Real Estate Exam Fees: $250 – $400
- REALTOR® Association Fees: Varies, but includes national dues, certification assessments, and potentially local and state association fees.
Operational Costs
- Broker and Desk Fees: Varies based on the brokerage.
- MLS Fees: $150 – $300 annually
- Errors & Omissions Insurance: $30 – $60/month
- Health Insurance: Around $450 for an individual and $1,150 for a family monthly.
Marketing and Client Acquisition
- Marketing Expenses: Initial costs can eaisly exceed $1,000 for the first year.
- Mileage and Vehicle Expenses: Approximately $1,200 monthly.
Taxes and Financial Management
- Income Taxes: Varies based on income and deductions.
Technology and Software
The real estate industry has seen a surge in the use of technology and software to streamline operations, manage customer relationships, and enhance marketing efforts.
This includes CRM systems, property management software, virtual tour software, and financial management tools. Depending on the complexity and features of the software, costs can range from $20/month for basic tools to $500/month or more for advanced, integrated systems.
In addition, many real estate companies now invest in custom software tailored to their specific needs, which can have an initial development cost but offer long-term benefits in terms of efficiency and scalability.
How to start a real estate business in 15 steps
Since we have all the basics covered let’s finally move on to what matters: 15 steps to guide you through the process.

Step 1: Pick a specific niche
Entering the real estate business requires strategic focus, and the selection of a specific niche becomes critical in this endeavor.
Focusing on a particular niche, such as residential, commercial or investment real estate, allows new businesses to concentrate their efforts, resources and expertise, thereby enhancing their competitive edge and quality of service.
Key examples of popular niches in the real estate market:
- Residential real estate and condos,
- Resort and vacation homes,
- Income properties,
- Luxury real estate,
- Commercial zones,
- Property management
Specializing in a defined niche enables the agency to develop in-depth knowledge, tailored strategies, and specialized services that cater to the specific needs and preferences of a particular client segment. This focused approach not only facilitates the optimization of resources and marketing efforts but also ensures that the agency can establish itself as an authority in the chosen domain, thereby building credibility and attracting a targeted client base.
It is imperative to underscore that while diversification into multiple niches may offer varied opportunities, it also disperses focus and resources, potentially diluting the agency’s expertise and brand positioning, especially in the initial stages of business development.
[Read also: A Step-by-Step Guide: How to Start an Online Travel Agency (OTA)]
Step 2: Do extensive research
Any business, regardless of the market, should always begin with extensive research.
This also applies to the real estate business.
Comprehensive research enables the agency to gain insights into the chosen niche, understand market dynamics, identify potential opportunities and anticipate challenges, thereby formulating informed strategies that enhance operational efficiency and market positioning.
It is imperative to examine various facets of the market, including customer demographics, competitor strategies, regulatory compliance, and emerging trends, to ensure that the business model, service offerings, and marketing strategies are congruent with market demands and opportunities.
Points to consider during the research phase:
- Client Demographics: Identify and understand the target client base, their preferences, and requirements.
- Competitor Analysis: Scrutinize strategies, strengths, and weaknesses of existing competitors in the niche.
- Market Trends: Analyze current and emerging trends that could influence the market and client behavior.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understand legal and regulatory requirements pertinent to the real estate industry.
- Pricing Strategies: Investigate prevailing pricing and commission structures within the niche.
- Technology Utilization: Explore technological tools and platforms that can optimize operations and client engagement.
- Risk Factors: Identify potential risks and challenges within the niche and develop mitigation strategies.
Step 3: Create a real estate business plan
Now is the time for one of the most important steps – a business plan.
The creation of a robust real estate business plan is critical, serving as a strategic blueprint that outlines the agency’s goals, operational framework, and financial strategies, ensuring a structured approach to business development and management.
Take time to think about your business and answer the following questions:
- What is your company’s vision and mission?
- What is your value proposition?
- Which of your customer’s problems are you helping to solve?
- How will you make a difference for yourself, your clients, and the world?
- How do you differenciate yourself from the competition?
- How do those principles and values differentiate it from other businesses?
- Who will be your key partners and clients?
- What are your revenue streams?
A carefully crafted business plan not only provides clarity and direction for internal operations, but also serves as a compelling tool when engaging with external stakeholders such as investors, partners, and financial institutions.
It encapsulates the agency’s value proposition, market strategies, operational processes, and financial projections, providing a comprehensive view of the business and its strategic direction.
Ten key elements to include in a real estate business plan:
- Executive Summary: A succinct overview of the business, its objectives, and value proposition.
- Business Description: Detailed information about the business, its mission, vision, and objectives.
- Market Analysis: Insights into market conditions, trends, client demographics, and competitor strategies.
- Services and Offerings: Description of the services and offerings provided by the agency.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Comprehensive strategies for marketing, sales, and client acquisition.
- Operational Plan: Detailed plan for daily operations, technology utilization, and client management.
- Financial Projections: Projected income, expenses, and financial forecasts for the business.
- Risk Analysis: Identification of potential risks and corresponding mitigation strategies.
- Growth and Expansion Strategy: Strategic plan for future growth, diversification, and expansion.
- Metrics and Performance Evaluation: Mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating business performance.
Step 4: Create a sales plan
A sales plan, while an integral part of the overarching business strategy, focuses specifically on the mechanisms and strategies to achieve the agency’s revenue goals within a specified timeframe.
It is a tactical document that outlines the agency’s sales goals, target clientele, sales strategies and mechanisms for lead generation, conversion and retention.
Unlike the general business plan, which provides a comprehensive overview of the entire business operation, the sales plan focuses exclusively on detailing the strategies and activities that will drive sales and revenue generation.
It highlights the ways in which the agency will attract, engage and convert prospects into clients, thereby ensuring a steady stream of revenue and facilitating financial stability.
The sales plan should be carefully crafted to align with the agency’s service offerings, market conditions, and client preferences to ensure that sales strategies are not only viable, but also resonate with the target clientele, thereby optimizing sales effectiveness and increasing revenue generation.
Step 5: Choose a legal business structure
The selection of an appropriate legal entity structure is paramount in the formation of a real estate agency, as it dictates the regulatory compliance, tax obligations, liability implications and operational dynamics of the business.
The choice of legal structure should be carefully aligned with the agency’s operational scale, financial management and risk mitigation strategies to ensure it provides an optimal framework for business operations and growth.
Different legal structures offer different benefits and limitations, and understanding these is critical to making an informed decision that protects the agency’s interests and facilitates its strategic objectives.
Possible choices for legal structures and their pros and cons:

Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a straightforward business structure, owned and operated by a single individual, offering ease of management but placing all business liabilities directly on the owner.
- Pros: Simple setup, complete control, straightforward tax filing.
- Cons: Unlimited personal liability, potential difficulty in raising capital.
Partnership
A partnership involves two or more individuals jointly owning and managing the business, sharing profits, responsibilities, and liabilities, while benefiting from combined resources and expertise.
- Pros: Shared responsibility, pooled resources, combined expertise.
- Cons: Potential for conflict, joint liability for debts and actions.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC combines features of corporations and partnerships, providing owners with limited liability protection while offering operational flexibility and varied tax options.
- Pros: Limited liability, flexible tax options, operational flexibility.
- Cons: More complex setup, potential state-imposed limitations.
Corporation
A corporation is a legal entity separate from its owners, providing them with limited liability, and has the ability to raise capital through the sale of stock, albeit with stringent regulatory compliance and reporting obligations.
- Pros: Limited liability, enhanced credibility, easier capital generation.
- Cons: Complex and costly setup, rigorous regulatory and reporting requirements.
S Corporation
An S Corporation provides owners with limited liability and allows profits and losses to be passed through to shareholders’ personal tax returns without subjecting them to corporate tax rates, while adhering to specific eligibility criteria.
- Pros: Limited liability, tax benefits, transferable stock.
- Cons: Eligibility restrictions, stricter operational guidelines.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP is a partnership structure where partners have limited liability, protecting them from the actions and debts of the partnership, while allowing them to maintain control over the business operations.
- Pros: Limited liability, shared control, flexibility in the distribution of profits.
- Cons: Complexity in setup, varied regulations across jurisdictions.
[Read also: How to Start a SaaS Company: Your Ultimate Guide]
Step 6: Obtain a real estate business license
Securing a real estate business license or real estate broker license is another fundamental step in establishing a real estate agency, ensuring that the business operates in compliance with regulatory standards and legal mandates.
The process of obtaining a real estate business license can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction, country, and sometimes even the city in which the agency intends to operate, each with its own set of requirements, processes, and regulatory bodies governing the real estate industry.
Complying with licensing requirements not only ensures legal compliance, but also enhances the agency’s credibility with clients and stakeholders by confirming its legitimacy and adherence to professional standards.
A general, sample process for obtaining a real estate business license might involve the following steps:
- Eligibility Verification: Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria, which may include age, educational qualifications, and residency status.
- Education and Examination: Complete any mandatory educational courses related to real estate practices and successfully pass the relevant licensing examination.
- Application Submission: Submit a license application to the relevant regulatory body, providing all necessary documentation and information.
- Background Check: Undergo a background check, as mandated by some jurisdictions to ensure the credibility of the license holder.
- Fee Payment: Pay the applicable licensing fees, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction and type of license.
- License Approval: Await approval from the regulatory body, upon which the license will be issued, enabling the commencement of real estate business operations.
Step 7: Choose office location and recruit your team
Now it is time to move on to more enjoyable activities – choosing a location for your business and recruiting a team that shares your vision.
Strategically selecting an office location and assembling a competent team are critical steps in establishing a real estate agency, each contributing significantly to its operational efficiency and market presence.
While the choice of office location has traditionally been critical to visibility and accessibility, its importance has evolved since the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. The rise of remote working models has reshaped conventional norms of workspace utility and customer interaction.
However, maintaining a physical office, especially in a location that resonates with the agency’s target market, remains relevant. An aesthetically pleasing and strategically located office not only serves as a tangible representation of the agency’s brand, but also provides a conducive environment for meeting with prospective clients and business partners, thereby enhancing opportunities for relationship building and collaboration.
At the same time, recruiting a team that aligns with the agency’s goals and culture is paramount. The team should consist of individuals who bring a blend of expertise, experience and innovation to ensure that the agency can provide comprehensive and quality services to its clients.
Step 8: Have your business insured
Ensuring that the real estate agency is adequately insured is imperative, providing a safeguard against potential risks, liabilities, and unforeseen contingencies that may impact business operations and financial stability.
The process of selecting suitable business insurance policies should be meticulous, ensuring that it align with the agency’s operations, scale, and risk factors, thereby providing optimal coverage and risk mitigation.
The main types of insurance to consider include:
- General Liability Business Insurance: Protects against claims of bodily injury, property damage, and related liabilities.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Covers claims arising from professional advice, services, or errors and omissions.
- Property Insurance: Safeguards the physical office space and its contents against damage or loss.
Step 9: Establish an online presence
In the era of digital transformation in real estate, establishing a robust online presence is essential for a real estate agency, serving as a primary conduit for client engagement, brand visibility and lead generation.
A strategic approach to online marketing ensures that the agency can effectively reach its target audience, engage with prospects, and showcase its service offerings, thereby optimizing its market position and revenue potential.
Not to get ahead of ourselves, but to stay on the right track to building a solid online presence, there are three key points that every aspiring real estate firm should consider:
- Starting a Marketing Strategy – Initiating a marketing strategy for a real estate agency begins with the development of a professional website, serving as the digital storefront that showcases property listings, client testimonials, and the agency’s services. Parallelly, it’s essential to establish a presence on key social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter, enabling direct engagement with potential clients and the broader audience and integrating search engine optimization (SEO) techniques.
- Running and Managing the Strategy – The continuous management of a marketing strategy demands the creation and dissemination of valuable content. Regularly publishing insightful blogs, engaging videos, and informative infographics not only educates the audience but also positions the agency as a thought leader in the real estate domain. To amplify reach, paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and Facebook can be deployed, targeting specific demographics and driving directed traffic.
- Current Trends in Real Estate Marketing – The real estate marketing landscape is continually evolving, with current trends emphasizing the integration of technology and user-centric approaches. Virtual tours have emerged as a pivotal tool, offering clients immersive 360-degree views of properties from the comfort of their homes. The rise of chatbots and artificial intelligence on agency websites facilitates instant, automated responses to client inquiries, enhancing user experience. Video content, ranging from property showcases to market insights, resonates deeply with audiences, driving engagement and recall.

Step 10: Select an accounting system
Now let’s talk about choosing the right accounting system – a critical decision for a real estate agency because it directly impacts financial management, reporting accuracy, and operational efficiency.
When selecting enterprise software, it’s important to consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, and features specific to real estate transactions.
While off-the-shelf software solutions offer standard functionality and quick implementation, they may not address the unique nuances and requirements of a specific real estate agency.
This is where the advantage of developing a custom solution comes into play.
A customized accounting system that is tailored to the agency’s specific needs ensures that all functionalities are precisely aligned with the business model, transaction types, and reporting requirements. Custom real estate software development offer flexibility, allowing for modifications and enhancements as the agency grows and its needs evolve.
If you are looking for a development team that is ready to create a custom solution that will meet the unique needs of your business, contact us and schedule a free consultation today!
Our software developers are experienced in developing high performance software for the travel, finance and real estate industries.
Step 11: Remember about technology and software integration
In the contemporary real estate landscape, technology and software integration play an indispensable role in streamlining operations, enhancing client engagement, and optimizing business outcomes. Different types of software solutions cater to various facets of the real estate business:
- Property Management System: These platforms allow agencies to showcase properties, manage listings, and engage with potential buyers or renters.
- Document Management Systems: Given the plethora of documents in real estate transactions, these systems help in organizing, storing, and retrieving essential documents seamlessly.
- Analytics and Reporting Tools: These provide insights into market trends, client behavior, and business performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Virtual Tour Software: In the digital age, offering virtual property tours has become a norm, and the right software ensures high-quality, immersive experiences for clients.
And just as in the previous step, while off-the-shelf software solutions address general needs, a tailored, customized approach offers distinct advantages. Custom software solutions are designed to fit perfectly with the agency’s specific operating model, ensuring that every feature and functionality is tailored to the unique needs of the business.
Step 12: Implement Client Relationship Management (CRM) System
In the real estate industry, where customer interactions, relationship building, and transaction management are at the core of business operations, implementing a robust customer relationship management (CRM) system isn’t just beneficial – it’s essential.
The importance of CRM systems in real estate cannot be overstated, and that’s why they deserve their own step on our list.
They serve as a central hub for managing customer interactions, tracking leads, facilitating communication, and ensuring that every customer touchpoint in real estate is captured and optimized. Given the long-term nature of real estate transactions and the importance of repeat and referral business, a CRM system ensures that agencies can nurture relationships, understand client preferences and provide tailored services, thereby increasing client satisfaction and loyalty.
Key features that a good real estate CRM software must include are:
- Contact Management: Store and organize client information, ensuring easy retrieval and segmentation.
- Lead Tracking: Monitor the source and status of leads, ensuring timely follow-ups and conversions.
- Property Matching: Match client preferences with available property listings, facilitating quicker sales or rentals.
- Communication Tools: Integrated tools for email, messaging, and calls, ensuring seamless client communication.
- Task and Appointment Management: Schedule meetings, viewings, and follow-ups, ensuring no opportunities are missed.
- Document Storage: Organize and store essential transaction documents, contracts, and client communication.
- Analytics and Reporting: Gain insights into client behavior, sales performance, and market trends.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly integrate with other software tools, such as accounting systems, property listing platforms, and marketing tools.
- Mobile Access: Access the CRM on-the-go, ensuring real-time updates and client engagement.
- Automated Marketing: Automate marketing campaigns, newsletters, and client engagement activities.
Step 13: Keep track of financial management and budgeting
Financial management and budgeting are cornerstones of any successful business, and in real estate, their importance is magnified.
By its very nature, real estate is a high-value, illiquid asset. This means that while there is the potential for significant returns, there is also a significant amount of capital tied up in properties that can’t be turned into cash quickly.
As a result, maintaining a positive cash flow becomes essential.
A positive cash flow ensures that the agency can meet its operating expenses, service any debt, and invest in growth opportunities, even if there are delays in property sales or rentals. It provides a buffer against market downturns and ensures that the business remains solvent during difficult times.
In addition, in an industry where transaction timelines can be lengthy, a clear financial and budgetary plan ensures that funds are available for essential activities such as marketing, property maintenance and staff salaries, even if income from property sales or leases is still in the pipeline.
Effective financial management involves carefully tracking income and expenses, forecasting revenues, and anticipating potential financial challenges. Budgeting, on the other hand, ensures that funds are prudently allocated among various business activities to optimize resource utilization and ensure financial sustainability.
[Read also: What is GDS? Your Complete Guide to Mastering Travel Technology]
Step 14: Network and build partnerships
By now, your real estate business should be up and running.
Now it’s time to expand and improve.
In the real estate industry, where personal connections, trust, and collaboration play a pivotal role, the act of networking and forging strategic partnerships is essential.
Establishing a robust network provides a real estate agency with access to a broader clientele, insight into market trends, and opportunities for collaboration. It facilitates the sharing of knowledge, resources and leads, thereby expanding the agency’s reach and market presence.
Building partnerships, whether with other real estate professionals, financial institutions, legal experts or developers, can significantly enhance the agency’s service offerings. Such collaborations can lead to exclusive property listings, preferential loan rates for clients, streamlined legal processes, and access to off-market deals. Partnerships also provide a platform for co-marketing initiatives, sharing operational costs and leveraging combined expertise to navigate complex transactions.
Step 15: Continuously learn and monitor industry trends
At the end of this comprehensive journey of building a real estate business, the final, yet enduring step is a commitment to continuous learning and vigilant monitoring of real estate market trends.
The real estate landscape is dynamic, influenced by economic factors, technological advances, societal preferences, and regulatory changes. Staying attuned to these changes isn’t just a matter of staying current – it’s about ensuring the agency’s relevance, adaptability and future growth prospects.
By keeping their finger on the pulse of the market, agencies can anticipate change, adjust their strategies, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Whether it’s the rise of sustainable housing, the integration of smart home technologies, evolving buyer demographics, or shifts in investment patterns, staying ahead of the curve positions the agency as a thought leader and trusted advisor to its clients.
In addition, ongoing learning through professional courses, seminars, and workshops ensures that the agency and its team remain at the forefront of industry knowledge and best practices. This commitment to excellence and adaptability not only enhances the agency’s service offerings but also strengthens its reputation in the marketplace.
Business benefits of starting your own real estate company
Starting a real estate company can offer a multitude of business benefits. Here are some of them:
Revenue Potential
The real estate sector by nature offers substantial financial prospects, driven primarily by commission-based revenue models.
Establishing a real estate agency allows entrepreneurs to capitalize on multiple revenue streams, including transaction commissions, property management fees, and consulting fees. The agency can generate steady revenue by facilitating real estate transactions, managing rental properties and providing expert advice to clients, thereby ensuring a steady cash flow and potential for financial growth in burgeoning market conditions.
Entrepreneurial Control
Owning a real estate agency provides a high degree of entrepreneurial autonomy, allowing for direct oversight and control of business operations, strategic planning and decision-making processes. Entrepreneurs can formulate and implement business strategies that align with their vision and understanding of the marketplace, ensuring that the agency’s operations, marketing efforts and service offerings are tailored to target demographics and emerging market opportunities, thereby optimizing operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
Asset Accumulation
Involvement in the real estate industry provides an opportunity to accumulate tangible assets that can serve as a valuable financial reservoir.
The acquisition and management of real estate not only generates immediate income through rental or sale, but also acts as an appreciating asset, contributing to the long-term financial stability and wealth of the agency. Strategic real estate investments and prudent asset management can enhance the agency’s financial portfolio, providing both liquidity and collateral that can be used in future business ventures.
Building a Brand
Establishing a real estate agency allows entrepreneurs to build and maintain their own brand, which can be instrumental in gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
A well-cultivated brand, characterized by reliability, expertise and client-focused services, can enhance the agency’s market presence and credibility. Through strategic marketing, client testimonials, and consistent quality of service, the agency can strengthen its brand image, thereby attracting prospective clients, fostering loyalty, and facilitating repeat and referral business, which are essential for sustainable growth.
Networking Opportunities
Operating in the real estate industry inherently involves interacting with a wide range of stakeholders, including investors, developers, legal professionals and other real estate professionals.
Establishing a real estate agency provides ample networking opportunities that can be leveraged to forge strategic alliances, collaborate on joint ventures, and gain insight into emerging market trends and opportunities. Effective networking can facilitate access to exclusive property listings, investment opportunities and collaborative ventures, thereby enhancing the agency’s service offerings and market position.
Understanding real estate industry: key trends and statistics
Navigating through the real estate industry necessitates a robust understanding of its multifaceted nature, encompassing various sectors, each with its distinct dynamics and regulatory frameworks.
According to the National Association of Realtors, there were over 100,000 real estate brokerage firms operating in the US, in 2020. The same year, 5.64 million existing homes and 822,000 newly built homes were sold.
The substantial development rise in the real estate market is not substantiated.
The prices of real estate in the US have been steadily rising for years.
Since 1990, median house prices in the US have experienced a significant increase, driven by factors such as inflation, economic growth, and demand-supply dynamics in the housing market.
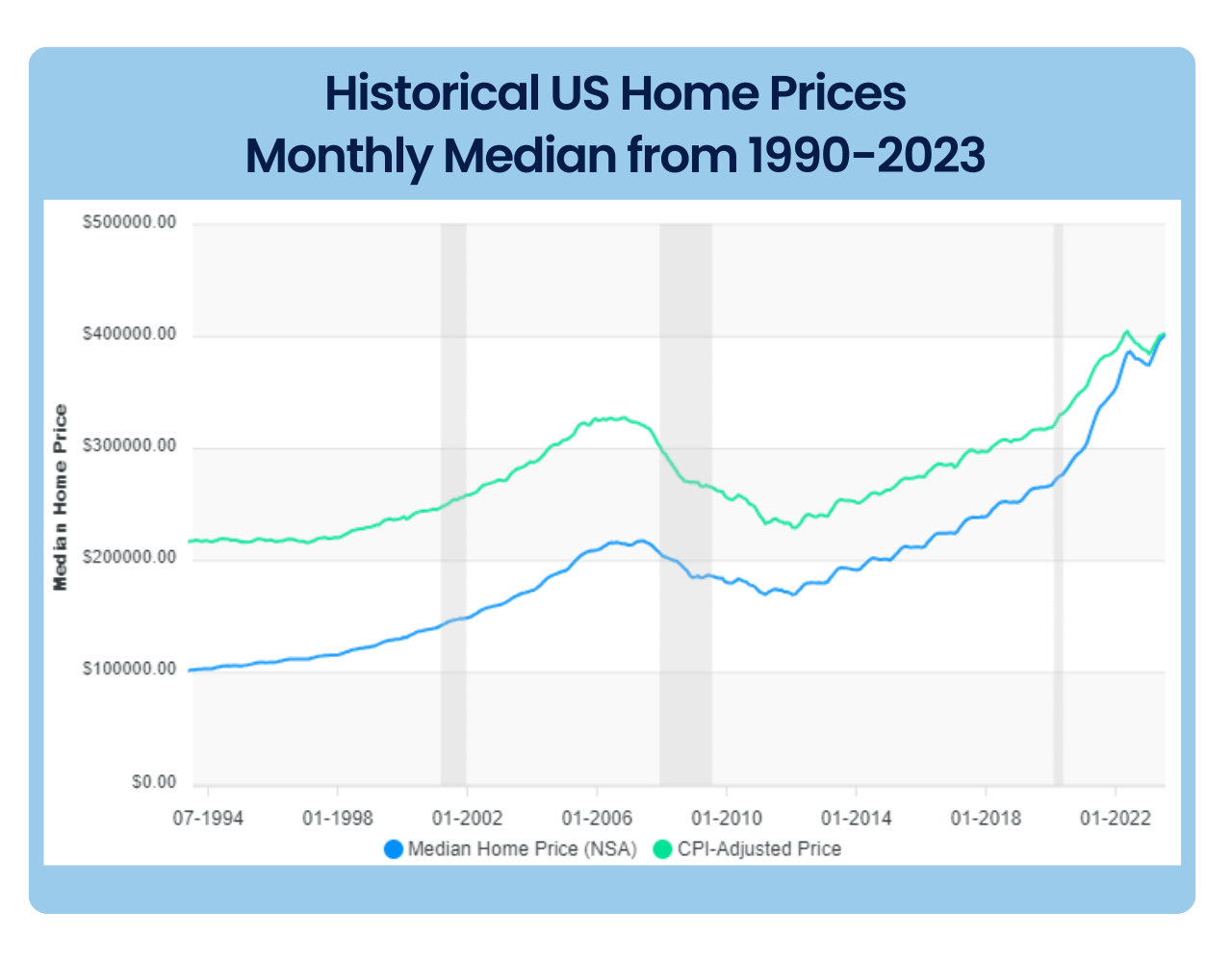
Source: Historical US Home Prices: Monthly Median from 1953-2023
Over the years, there have been periods of faster growth, especially in the early 2000s and post-2012, interspersed with periods of slower growth or decline, such as during the housing crisis of 2008. The median house price has reached new highs in recent years, with values peaking in 2022.
In 2024, the real estate companies are poised to evolve, influenced by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and global economic shifts.
The integration of digital platforms, adoption of sustainable practices, and the emergence of alternative living and working spaces are shaping the future trajectory of the market.
Moreover, the global real estate market, while still recovering and adapting to the aftermath of the pandemic, is expected to witness transformative trends, such as the rise of remote working influencing residential and commercial property dynamics, and the increasing significance of e-commerce impacting retail spaces.
Conclusion
Building a successful real estate business is no easy feat.
The journey requires thorough market research, a well-thought-out business plan, and an unyielding determination to navigate the industry’s inherent challenges.
With the right mix of diligence, networking, and adaptability, aspiring real estate entrepreneurs can build a solid foundation for a thriving and resilient business in today’s market landscape.
Related Posts
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog post!