
Payment Integration: A Comprehensive Guide to Payment Gateway
In recent years, the world of commerce and other services has moved inexorably into the virtual space, and online businesses have become increasingly popular. Whether it is a SaaS application or an online store, users need a convenient way to pay for goods and services online.
As the demand for seamless online transactions continues to grow, the importance of payment gateways cannot be overstated.
In this article, we explore the world of payment integration, examine its importance, and identify the key elements that contribute to the growth of successful online businesses.
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway serves as a bridge between online merchants and customers, facilitating the secure and efficient transfer of funds during the checkout process.
Essentially, it is a virtual terminal that allows businesses to accept payments from a variety of sources, including credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, and more. Acting as a shield against potential cyber threats, payment gateways use advanced encryption and security measures to protect sensitive financial data, instilling confidence in both merchants and customers.
Payment gateway vs. payment processor
When discussing this topic, there are two key elements that are most often mentioned: payment processors and payment gateways. On the surface, they seem very similar and can easily be confused.
So what’s the difference?
We’ve already explained the latter of the two. Its main purpose is to connect a merchant’s website to a payment processor. It focuses on the security and transmission of sensitive payment information between customers, merchants, and financial organizations.
Payment processors, on the other hand, are responsible for processing and settling the payment transactions themselves.
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment processor is responsible for facilitating the flow of information between the customer’s bank or card issuer and the merchant’s bank to authorize and process the payment.
Once the payment is successfully authorized, the payment processor securely transfers the funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account and ensures that the funds are cleared and deposited into the merchant’s designated bank account.
In addition, there are specialized payment processors that handle complex back-end operations such as fraud detection, risk assessment, and compliance with payment industry regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
In summary, payment processors handle the technical and financial aspects of processing transactions and transferring funds, while payment gateways focus on the secure transfer of payment data between customers, merchants, and payment processors.
Together, they form a critical part of the online payment ecosystem, ensuring smooth and secure transactions for businesses and customers.
Payment gateways statistics
To better understand what payment gateways are and what role do they play in the modern economy let’s take a look at these statistics:
- According to Statista, the market size of payment gateways in selected countries worldwide in 2023 was estimated to be as follows: United States ($1.2 trillion), China ($0.8 trillion), Japan ($0.4 trillion), Germany ($0.3 trillion), and United Kingdom ($0.2 trillion).
- McKinsey report shows that, the global payments revenue grew by double digits for the second year in a row, reaching more than $2.2 trillion in 2022. The report also identified four key trends that are shaping the future of payments: instant payments, digital wallets, open banking, and decentralized finance.
- According to a report by Global Market Insights, the worldwide payment gateway market size surpassed USD 27 billion in 2022 and is estimated to expand at over 23% CAGR from 2023 to 2030 due to growing internet access and the shifting preference toward e-commerce services. The report also segmented the market by type, application, and region.
How do payment gateways work?
We already know what an online payment gateway is, but how does it really work? What happens from the time the customer clicks the “Pay” button until the money arrives in the merchant’s account?
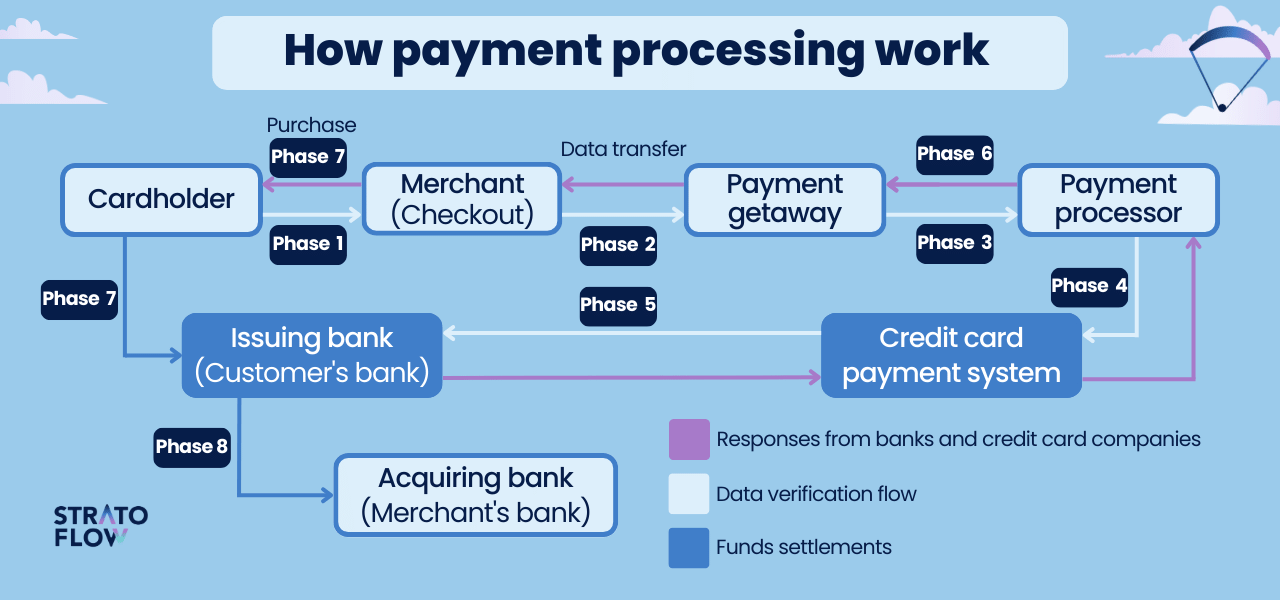
Let’s identify the key stages of the online payment process:
Phase 1: Customer is finalizing the purchase
It all starts when the customer clicks the “Buy” button on the merchant’s website and fills in all the necessary fields to submit the transaction data, including the cardholder’s name, card number, expiration date, and Card Verification Value (CVV) number. The data is then encrypted and sent over a secure SSL connection to the merchant’s web server.
Phase 2: Encryption in the payment gateway
Once the transaction data is received, the merchant sends it to the payment gateway via another encrypted SSL channel. If any of the data is stored by a payment gateway, it is handled in a special type of secure storage.
Phase 3: Going through the payment processor
The information then goes directly to the payment processors. As we’ve already explained, these are the third-party tools that actually process payment services. Payment processors are connected to both a store’s account and its payment gateway, transferring data back and forth. At this stage, the transaction information is sent to the card network (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc.).
Phase 4: Verification by the card network
In the fourth phase, the card network takes center stage and again verifies the transaction data and then forwards it to the issuer bank (the bank that manages the cardholder’s credit/debit card).
Phase 5: Authorization by the issuer bank
After that, the issuer bank finally accepts or denies the authorization request, which then transmits the message to the merchant. When the authorization process is completed, the merchant can “capture” the amount for the purchase from the buyer to the merchant account. The customer will not be billed until the capture has occurred, but the funds will be kept on hold.
Phase 6: Going back to the payment gateway
Once the authorization process is complete, the transaction status is returned to the payment gateway and then forwarded to the website.
Phase 7: Confirmation of the transaction status
In the last step of the payment process itself, the customer receives a message with the transaction status via the system interface.
Phase 8: Transferring the funds to the issuer bank
Within a few days, the funds are transferred to the merchant’s account, but it usually doesn’t take more than a single business day. The transaction is sent from the issuing bank to the acquiring bank.
Key types of payment gateways
Keep in mind that not all payment gateways are created equal, and understanding the main types available is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their payment processing capabilities.
Let’s look at three of the most common ways to integrate a payment gateway into your website:
Redirect Payment Gateways
With this type, when a customer is ready to make a purchase and selects their preferred payment method, they are redirected from the merchant’s website to the payment gateway’s platform to complete the transaction.
The customer enters their payment details on the secure gateway page, and after the payment is processed, they are redirected back to the merchant’s website. This approach ensures that the merchant does not directly handle or store sensitive payment information, reducing their security burden.
On-site Payment Gateways
On-site payment gateways, also known as integrated payment gateways, allow customers to complete the entire payment process without leaving the merchant’s website.
The payment form is integrated directly into the checkout page, providing a seamless and consistent user experience by eliminating the need for users to deal with loading screens and changing color schemes. While this integration provides more control and branding opportunities for the merchant, it also requires a higher level of security compliance since they are handling and transmitting payment data.
Off-site Payment Gateways
Off-site payment gateways, also known as self-hosted payment gateway, involve a third-party platform that handles the entire payment process on its servers.
When a customer is ready to pay, they are redirected to the gateway provider’s secure payment page to enter their payment information. Once the transaction is complete, the customer is redirected back to the merchant’s website. Off-site gateways are easy to implement and relieve the merchant of security concerns because payment data is managed off-site.
7 reasons to switch to an integrated payment solution
As you could probably imagine switching to an integrated payment gateway provider can offer numerous benefits to businesses.
Here is a list of key reasons to make the switch:

1. Streamlined checkout process
Integrated payment solutions provide a seamless and efficient checkout experience for customers. With the payment form directly integrated into the merchant’s website, customers can complete their transactions without being redirected to external payment pages, reducing the chances of cart abandonment.
2. Enhanced user experience
Integrated payment gateways offer a consistent and branded user interface, reinforcing trust and familiarity with customers. A user-friendly checkout process can lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased chances of repeat business.
3. Increased security
Integrated payment gateways also need to adhere to stringent security standards, protecting sensitive payment information.
By handling transactions on their own secure servers, these solutions help reduce the risk of data breaches and fraud, easing the burden of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance for merchants.
4. Faster payment processing
Integration allows for real-time payment processing, enabling quicker authorizations and reducing the time between transactions and fund settlements. This speed is especially beneficial for businesses with high transaction volumes.
5. Seamless integration with existing systems
Many integrated payment solutions are designed to easily integrate with existing ecommerce platforms, point-of-sale systems, and other business tools. This makes the transition smoother and reduces the need for significant changes to the existing infrastructure.
6. Reduced cart abandonment
A streamlined and secure checkout process payments with familiar branding can help reduce cart abandonment rates, as customers are more likely to complete their purchases without encountering unexpected hurdles.
7. 24/7 Customer Support
Reputable integrated payment solution providers usually offer reliable customer support, helping businesses resolve any payment-related issues promptly and ensuring smooth operations.
Top 5 payment gateway providers
When it comes to doing business online, choosing the right payment gateway provider is paramount. Seamless and secure transaction processing can make all the difference in creating a positive experience for both merchants and customers.
Let’s explore the leading contenders that continue to set the standard for secure payment integration in the digital age.
Stripe
Stripe is one of the most widely-used and developer-friendly payment gateways that offers a robust platform for online payment processing. It is known for its easy-to-integrate API, making it a popular choice among businesses and developers.
Stripe supports various payment methods, including credit card payments, debit cards, and digital wallets, and it operates in over 135 currencies, allowing businesses to operate globally. With advanced security features like encryption and tokenization, Stripe ensures the protection of sensitive payment data. It also provides real-time reporting and analytics for businesses to track transactions and performance.
Hotpay
HotPay is a popular Polish payment service provider that offers remarkable throughput achieved through a cloud-based infrastructure system.
This allows it to process hundreds of thousands of transactions in an instant. Thanks to this, HotPay can support payments during extremely high user activity, such as booking live events, concerts and festivals. It also offers a relatively low commission in the standard offer for a registered business (0.95%) – regardless of the size of the business and without negotiation.
Square
Square is a versatile payment gateway that handles both online and in-person payments. It offers a comprehensive solution for businesses, including point-of-sale (POS) systems, mobile card readers, and e-commerce payment processing. Square is known for its easy-to-use interface and transparent pricing.
PayPal
PayPal is one of the most recognized and widely used online payment tools in the world. It allows customers to make payments using their PayPal accounts or credit/debit cards.
PayPal’s widespread acceptance and consumer trust make it a popular choice for online merchants. It offers easy integration with various e-commerce platforms and provides buyer and seller protection programs for secure transactions. Despite its widespread use, PayPal’s transaction fees can be relatively high for certain types of transactions.
Adyen
Adyen is a global payment gateway designed for larger enterprises and high-volume merchants. It offers a unified platform that supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies, making it an ideal choice for businesses with international operations.
Adyen places a strong emphasis on security and employs advanced fraud detection and prevention tools. It also supports multi-channel payment processing for online, in-store, mobile and in-app payments, providing a seamless and unified shopping experience for customers.
How to set up swift payment integration: Openkoda case study
Alright, we’ve covered all the theoretical details about online payment gateway providers, but one key question remains unanswered: how to integrate a payment gateway into a website.
Let’s take a look at how it’s done in Openkoda – an open source low-code platform. But first, let’s see how it’s done in a usual way.
Typically, integrating a payment gateway with an online store website or any other website involves several key steps to ensure smooth and secure transactions for customers.
First, you need to register an account with the chosen provider and obtain the necessary credentials, most importantly the API keys. Next, you need to ensure that your website’s platform or content management system (CMS) supports your chosen payment gateway or provides plug-ins for easy integration. Install the appropriate plugin or integrate the gateway manually using the provided APIs. This part requires some work from a software developer. How much? Well, it depends on the API itself and how much customization we want to do in our web application. However, it’s quite a lot of work for such a basic feature of an online application.
With Openkoda it’s quite a different story.
This AI-powered open source low-code platform has dedicated modules that can be integrated into existing software development projects. These modules include ready-made integrations with Stripe – one of the most popular online payment gateways.
We won’t get into all the technical details of the integration process in order not to make it too overwhelming for you, but keep in mind that this approach is much faster and more efficient than manually connecting to the payment API, and it accomplishes virtually the same thing – enabling users to make payments on your web application.
Another great advantage of Openkoda payment gateway integration is the ease of switching between different online payment providers. The core data model and backend logic are common to all service providers. So if for whatever reason you need to switch to another payment gateway company, you can do it very quickly and efficiently without worrying about another lengthy API integration process.
In other words, with Openkoda you save extremely valuable developer time by using pre-built payment integration – an advantage that is invaluable in today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment.
However, if you lack any technical knowledge regarding programming, don’t be afraid to seek the help of a custom software development company. A team of highly experienced programmers will guide you through all the intricacies of the software development lifecycle and provide you with the most efficient approach for your unique business scenario.
Conclusion
Payment integration solutions are undeniably the backbone of online businesses in the modern e-commerce and SaaS business landscape.
As we’ve explored their importance, it’s clear that seamless and secure payment processing is not just a convenience, but a necessity to thrive in the competitive world of e-commerce and SaaS applications. By providing customers with a smooth checkout experience and protecting their sensitive data, payment integration fosters trust, loyalty and repeat business.
Related Posts
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog post!
FAQ
What is payment gateway integration?
Payment gateway integration refers to the process of connecting a payment gateway to a website or an application, enabling the acceptance and processing of online payments. It involves integrating the gateway’s software or API (Application Programming Interface) into the website’s checkout system, allowing customers to securely enter their payment information and complete transactions with ease.
How much does a payment gateway cost?
Payment gateways usually apply a mix of initial setup charges, a fixed monthly fee, and a small per-transaction fee. Some gateways may also deduct a percentage from each purchase. For instance, Square imposes a 10-cent fee on most card transactions in addition to 2.6% of the payment volume. Stripe, on the other hand, charges 2.9% along with 30 cents per transaction. Furthermore, additional fees might apply for equipment and installation.
What is a white-label payment gateway?
A white label payment gateway is a payment processing solution offered by a company that allows other businesses to use the service under their own branding. The white label provider handles the technical aspects of payment processing, while the partnering business can customize the gateway’s user interface to match its branding, providing a seamless and branded payment experience for its customers.
Is PayPal a payment gateway or processor?
PayPal is both a payment gateway and a payment processor. As a payment gateway, it serves as a secure bridge between a merchant’s website or application and the customer, facilitating the secure transmission of payment information during the checkout process. As a payment processor, PayPal handles the actual movement and settlement of funds, transferring money from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account upon successful payment authorization.
