
Software Development Process: Complete 2025 Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to the software development process – your essential resource for understanding the world of software development.
In this guide, we explore each stage of the software development lifecycle, unpack the pros and cons of custom software versus off-the-shelf solutions, and introduce cutting-edge alternatives like Openkoda for a faster and more cost-effective software development process.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a business executive looking for technical insights for your next project, this guide is designed to provide you with valuable insights and practical knowledge. Dive in and discover the keys to successful software development in today’s fast-paced digital world!
Contents
- What is an AI-powered recommendation system?
- What is a software development lifecycle (SDLC)?
- The importance of well-defined software development processes
- Six key stages of the software development process
- How to speed up the software development process
- Top software development methodologies worth knowing
- Types of software development approaches
What is the software development process?
The software development process is a structured approach to creating and maintaining software applications.
It typically involves several software development stages:
- Software development planning stage
- Software design stage
- Software development and coding stage
- Software testing stage
- Software deployment stage
- Software maintenance stage

You can say that the software development process is like building a house but in the digital world – each phase of the software development process corresponds with a key part of the construction process.
No wonder why software developers are often called architects.
First, you need to have a clear plan or idea, just like an architect’s blueprint for a house. This plan includes what the software will do and who will use it.
Then, developers, who are like the construction workers for software, start writing code, which is like the building blocks for the software.
This whole process is essential in the business world because it leads to the creation of useful tools and applications that help companies and individuals do their work more efficiently and effectively.
What is a software development lifecycle (SDLC)?
A software development lifecycle (SDLC) is a series of steps that guide the creation of software in a systematic and efficient manner.
You can think of it as a roadmap for developing software while ensuring quality and efficiency in the process.
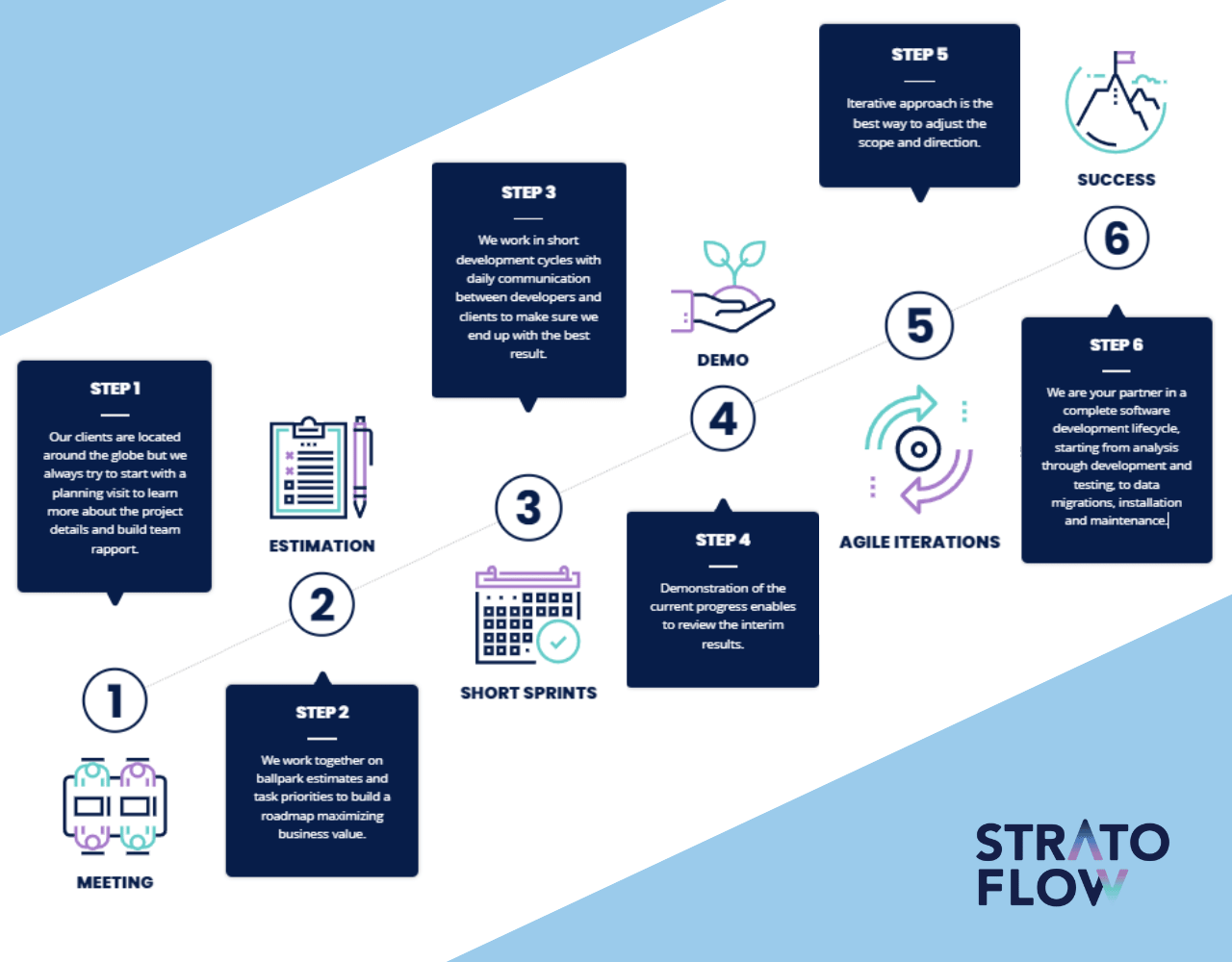
What are the steps of the development process for a software project?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for a software project typically unfolds in several key steps each corresponding to a different phase of the software development process.
This cycle is iterative, meaning that it can circle back to earlier stages as new requirements arise or problems are discovered, ensuring continuous improvement of the software project.
The importance of well-defined software development processes
Having well-defined software development processes is critical to the success of custom development projects and ensuring a smooth workflow.
These processes act as a roadmap that guides the team through each stage of development, from initial planning to final deployment. They ensure that every aspect of the software is carefully thought out, designed, and tested, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring that the final product meets the specific needs for which it was designed.
A well-defined software development processes result in higher quality software, improved customer satisfaction, and a more efficient and productive development team.
[Read also: The Complete Guide to Software Outsourcing: How to Make it Work for Your Business]
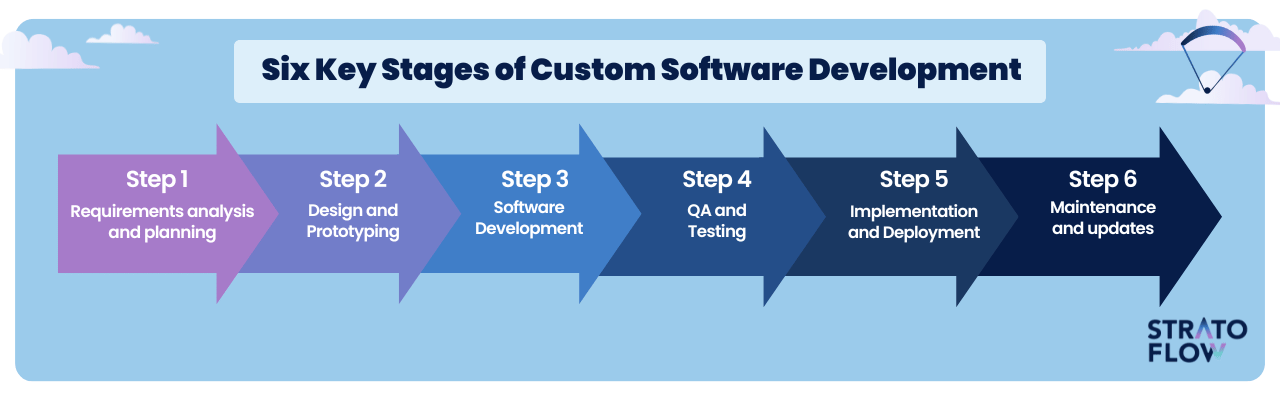
Six key stages of the software development process
As we delve into the specifics of software development, let’s explore the six key stages that form the backbone of any successful software development process.
From initial planning to final deployment, each stage plays a critical role in transforming a concept into a working software product.
Stage #1: Requirements analysis and planning
This first phase of the product development life cycle is all about understanding what the software needs to do.
This step is usually referred to as requirement analysis and software development planning.
Start by diving deep into understanding your business’s specific needs and what your users expect. This means working closely with stakeholders to gather detailed requirements, including functional, technical, and operational aspects. It’s not just about what the software should do—it’s about how it should perform in different scenarios.
At this stage, you’ll make a critical decision: choosing the right software development methodology and approach.
This choice shapes how your project will be executed, influencing collaboration, development stages, and how changes are managed. Selecting the right methodology is crucial because it ensures alignment with your project goals, team dynamics, and overall business strategy.
What methodologies can your software development team choose from?
There are eight popular options, and we’ll explore some of them in more detail later in this article.
- Agile methodologies
- Scrum approach
- Waterfall software development methodology
- Lean system development methodology
- Kanban approach
- DevOps
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Stage #2: Design and Prototyping
The second phase is where the conceptual ideas and requirements take shape – the software development planning phase begins.
In this phase, the development team creates a detailed software architecture that outlines the technical specifications, data flows, user interface designs, and system functionalities. It’s a critical phase where strategic decisions are made about the overall structure and behavior of the software.
During this stage, the development team need to pick their tech stack and the supporting technologies like Java for the core and Kafka, Hazelcast and Oracle Coherence for IMDG data processing.
Two important components often included in the design phase are the Proof of Concept (POC) and the Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
A POC (Proof of Concept) is a small exercise that lets you test a specific concept or theory during the software development process. Essentially, it’s a prototype created by software engineers to prove the feasibility of certain aspects of your project. Building a POC is critical because it helps you validate technical assumptions, identify potential challenges, and assess the viability of your idea before committing significant time and resources.
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product), on the other hand, is a simplified version of the software that includes enough functionality for early users to try it out and provide feedback. It’s a fast, data-driven way to test a product or feature in the market. The MVP is crucial during the design phase because it focuses on core functionality, helping you understand what matters most to your users.
Incorporating a POC and MVP into your design phase is essential for reducing risks, optimizing resources, and ensuring your software is both market-ready and user-focused. These tools guide the development process to create a product that is not only technically sound but also valuable and aligned with user needs.
Stage #3: Software Development
Often considered the backbone of the software development process, coding phase is where developers bring the design to life by writing the actual program.
In this phase, developers translate the design blueprints into working software by writing code. This phase is critical because it involves turning the planned concept into a tangible product.
Clear communication with your project stakeholders is crucial to ensuring the software meets your business goals and user expectations.
Regular interactions with clients and stakeholders enable immediate feedback and adjustments, keeping the project aligned with your vision.
Using a methodology like Agile, which emphasizes short development sprints and an iterative approach, can be especially effective. These sprints typically last one to four weeks and involve daily communication between your team and the client.
This approach allows you to rapidly produce small, incremental updates to the software product.
It keeps the project moving in the right direction and helps you quickly address any issues or changes. Frequent collaboration ensures the software evolves to meet changing requirements and results in a final product that truly delivers value to your users.
The key takeaway is that in software development projects, there are three key values that must be the driving force of the entire process:
- Innovation,
- Collaboration,
- Agility.
Stage #4: QA and Testing

The software development testing phase is all about quality assurance.
During this phase, your software goes through rigorous testing to identify and fix bugs, errors, or other issues.
Software testing is crucial because it verifies that your software meets all requirements and performs as expected under different conditions. It’s a critical step in delivering reliable, user-friendly, and high-quality software.
Testing not only improves performance but also boosts user confidence and satisfaction by ensuring a smooth, error-free experience.
The main types of software testing include:
- Unit Testing: Checks individual components or pieces of code for proper operation.
- Performance Testing: Assesses the speed, responsiveness, and stability of the software under a particular workload ensuring the delivery of fast and efficient software.
- Integration Testing: Ensures that different modules or services used by the application work well together.
- Security Testing: This is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in the software to prevent potential attacks or breaches, ensuring the protection of user data and the integrity of the software.
- System Testing: Tests the complete and fully integrated software product to verify that it meets all specified requirements.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates how user-friendly and intuitive the software interface is for end-users.
Stage #5: Implementation and Deployment
Implementation and deployment phase is the stage where the software is fianally released to real users.
Think of it as the grand opening of a digital product.
Implementation involves integrating the software into the user’s environment, which may include setting it up on servers, configuring it for use, and sometimes migrating data from old systems to the new.
Deployment is the process of making your software available to users.
This could involve releasing it for download on public platforms, enabling online access, or distributing it internally within your organization.
This phase is critical because it’s the first time the software is used in a real-world environment, which may uncover issues that didn’t appear during testing. Careful planning is essential to ensure a smooth transition for users, minimizing disruptions to their operations.
Stage #6: Maintenance and updates
After the software is deployed, it enters the maintenance phase.
This involves regularly monitoring the software for problems, fixing bugs, and making necessary changes to improve performance or add new features.
Constant updates are essential during this phase, as they not only improve the software but also protect it from security vulnerabilities.
Regular updates help keep the software compatible with evolving technologies and changing user needs, preventing it from becoming outdated or obsolete. This is especially important to avoid the challenges of dealing with legacy software, which can be costly and inefficient to maintain.
Proper technical documentation at this stage is also critical. It provides a clear record of changes, updates, and the current state of the software, making future maintenance and enhancements easier and more efficient. This documentation is a valuable resource for any new team members or developers who may work on the software later.
[Read also: Application Modernization Strategy: Your Ultimate Guide]
How to speed up the software development process
Custom software development provides tailored solutions that perfectly align with your company’s unique needs, but it’s no secret that this approach can be both costly and time-intensive.
The significant investment of time and resources often makes custom development less accessible, especially for smaller companies or those with limited budgets.
To address this challenge, many organizations are exploring alternatives that offer the benefits of custom software while reducing the time and cost constraints.
One such alternative is the use of open source custom software development platforms such as Openkoda.

These platforms represent an evolution in approach to custom enterprise software development.
Openkoda, for example, enables rapid development of enterprise software applications by simplifying the programming process.
Such platforms provide pre-built modules and easy-to-use interfaces that enable faster and more efficient development of even complex applications.
This approach significantly reduces the amount of coding required, lowering both the skill barrier and the time investment. As a result, companies can develop custom software solutions much more quickly and cost-effectively, opening the door to custom software for a wider range of businesses.
Integrating platforms like Openkoda into the software development process is therefore a highly effective strategy for companies that want to enjoy the benefits of custom software without the traditional drawbacks of high costs and long development times.
By harnessing the power of low-code platforms, companies can accelerate their software development timelines, reduce costs, and still enjoy the benefits of software that is precisely tailored to their needs.
If you want to know more about how you can leverage the power of Openkoda platform in developing your own custom software applications, contact us!
Top software development methodologies worth knowing
In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the top software development methodologies that have shaped modern software development, from Agile to DevOps.
Understanding these methodologies is key to efficiently managing your development projects and adapting to the dynamic demands of the tech world.

Waterfall software development process
The oldest of all methodologies, the waterfall model is a linear and sequential approach to software development, where each phase must be completed before the next one begins.
It’s like a step-by-step process where you can’t go back to a previous step without starting over.
This method begins with a thorough planning and requirements-gathering phase, followed by design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
The waterfall model is straightforward and easy to understand, making it suitable for smaller projects with well-defined requirements. However, it lacks flexibility for changes once the project is underway, which can be a drawback in dynamic environments.
[Read also: Comprehensive Guide to Software Development Agreement [+Template]]
Rapid application development
RAD is a type of software development methodology that emphasizes rapid and iterative development.
It focuses on speed and flexibility, with less emphasis on detailed planning at the beginning of the project. In RAD, prototypes or usable segments of software are built quickly and continually improved through user feedback, making it a user-centered approach.
Spiral software development process
The Spiral model combines elements of both design and prototyping-in-stages.
It’s like a series of iterative cycles or ‘spirals’, where each one involves planning, risk assessment, engineering, and evaluation. This approach allows for multiple rounds of refinement, making it suitable for large, complex, and high-risk projects.
Agile software development methodology
Agile is a highly iterative and incremental approach to software development. It emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and small, rapid releases.
Agile model breaks the project into small chunks, with minimal planning, and emphasizes adaptability to change. This methodology is particularly effective in environments where requirements are expected to evolve or are not fully known at the start of the project.
Agile encourages a flexible, team-based approach where developers and business stakeholders work closely together throughout the project.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming is an Agile framework that aims to produce higher quality software and improve the quality of life for the development team.
XP emphasizes customer satisfaction and involves frequent “releases” in short development cycles, which improves productivity and introduces checkpoints where new customer requirements can be adopted.
DevOps
DevOps is not just a methodology but a culture or set of practices that emphasizes collaboration and communication between software developers and IT professionals.
The goal of DevOps is to automate and streamline the software development and infrastructure management processes.
Types of software development approaches
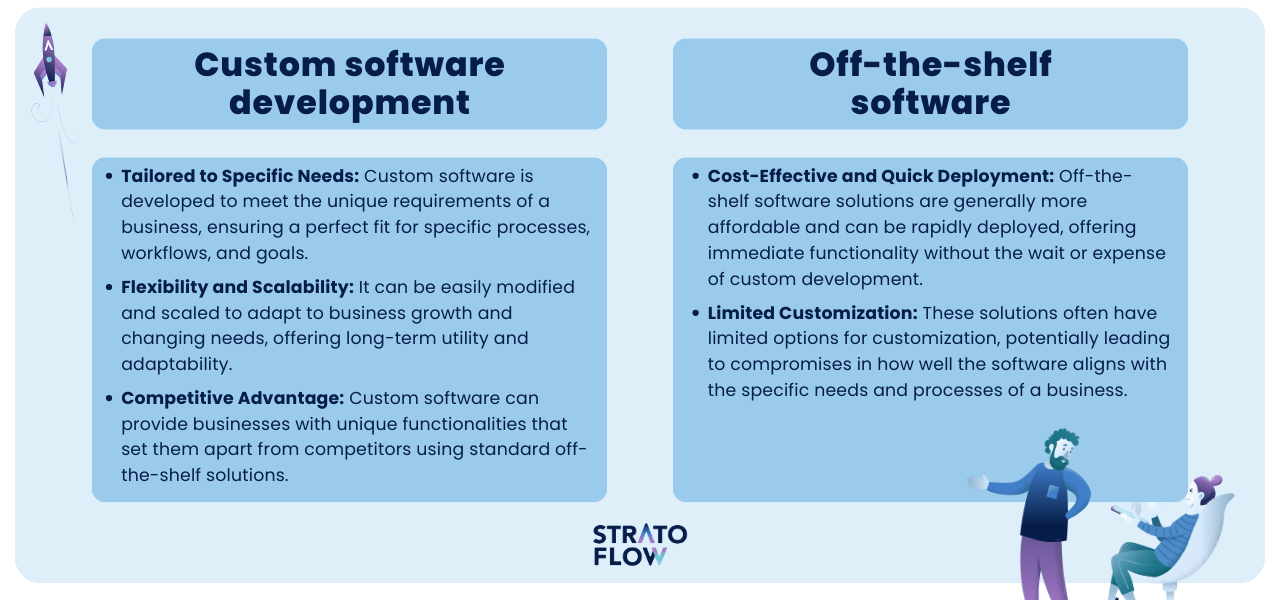
Custom software development vs off-the-shelf software represent two different approaches to meeting software needs in a business context, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Custom software development
Custom software development stands out as a highly advantageous option for companies seeking a precise solution tailored to their unique needs and processes.
It offers an unparalleled level of customization, allowing for software that is closely aligned with a company’s specific workflows, creating a perfect synergy with business operations.
This customized approach not only ensures efficiency and user satisfaction, but also provides the flexibility to adapt and scale the software as the business evolves – a critical aspect in today’s dynamic market environment.
While the initial investment in time, resources and money for custom software may be higher, this is offset by the significant long-term benefits of having a solution that fits the business perfectly.
Off-the-shelf software
While off-the-shelf software may seem cost-effective and convenient for immediate deployment, it often results in compromises in functionality and efficiency.
These generic solutions may include unnecessary features or lack critical business-specific functionality, resulting in a less-than-optimal fit.
Relying on outside vendors for updates and support can also be a challenge, especially if the product is discontinued or doesn’t evolve with the company’s changing needs.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our journey through the software development process, we hope you’ve gained a deeper understanding of the various stages, methodologies, and innovative approaches in software development.
From the meticulous planning in the initial stages to the agility offered by Agile methodologies, and the cutting-edge solutions like Openkoda, this guide aims to empower you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of software development.
Related Posts
- How to Build a Document Management System: Alternative Approach
- How to Find and Hire Full Stack Developers in 2025
- How To Hire Dedicated Developers in Europe [Benefits & Models]
- How to Prepare a Successful Application Migration Project
- Best AI for Coding: Top 10 AI Tools for Software Developers in 2025
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog post!
