
How to Perform Successful Website Security Audit: Checklist & Essential Tools
A website security audit like a health check for your website. Just like we go to the doctor, websites need check-ups too. This article talks about how these security check-ups (audits) work, why they’re important, and the steps and tools employed to maintain website security.
What is website security audit?
A website security audit is a comprehensive process that evaluates and analyzes a website for security vulnerabilities, threats, and risks.
In other words, website security audit is a process of scanning your website to identify loopholes and vulnerabilities.
The reason is simple. Every website owner has to prevent cyberattacks. Conducting regular website security audits ensures the security and integrity.

Website security audit vs. web application security audits
A website security audit goes beyond the application itself to include the hosting environment, server setup, network security, SSL/TLS certificates, and any related services such as content management systems (CMS) and their plug-ins.
This audit assesses server and network setups, assures adherence to security protocols, and checks physical server and data center safety if necessary.
The primary goal is to protect the entire website and infrastructure from various cyberattacks. When conducting a website security audit, it is essential to concentrate on operation aspects, like server setups, domain security, and CMS weaknesses.
A web application security audit, on the other hand, focuses only on making web applications secure.
Web application security scans check the software and application-level aspects. These are elements such as application code for vulnerabilities like SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, issues with authentication and authorization mechanisms, session management, data validation, API security, and the overall logic and business rules of the web application.
The goal is to find and fix vulnerabilities in the web application, to prevent attacks at the application level.
Since we understand the difference, let’s focus today on the website security audit process. In the upcoming article, we will take a closer look at web application security audits.

Why should you conduct web security audits? List of benefits
Web security audits offer many advantages and play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and integrity of online systems.
Some key advantages include:
Identification of vulnerabilities
Audits systematically uncover weaknesses in a website that could be exploited by cyberattackers. This early detection allows for timely remediation before any damage occurs.
Enhanced security
By addressing the website vulnerabilities found during a web security audit, the overall security of the website is significantly improved, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Compliance with regulations
Regular security audits ensure that websites comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy, such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc. This compliance is crucial for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining trust.
Protection of sensitive data
Audits help protect sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, and personal information. Maintaining confidentiality and preventing data leakage is where your website security audit can help your customers and users.
Improved user trust and credibility
A secure website or application fosters trust among users and customers. Knowing that a site is regularly audited and secure can enhance its reputation and credibility.
Prevention of financial loss
Security breaches often result in significant financial loss due to data theft, legal penalties, or business interruption. By aligning with the organization’s security policies, audits help prevent such incidents and their potential consequences, and protect the financial health of the organization.
Enhanced performance and uptime
Addressing security issues can also improve the performance and reliability of a website or application, ensuring better uptime and user experience.

Website security audit checklist
Before beginning a website security audit, it’s important to identify the specific elements of the site that need to be examined.
To ensure a thorough examination, the following website items should be included in a web audit checklist:
1. Core website framework
The audit begins with a detailed examination of the website’s basic structure and code base.
This includes a review of the platform or content management system (CMS) used to build the site, such as WordPress or Joomla.
The focus is on identifying any inherent vulnerabilities in the framework, including insecure coding practices, use of outdated libraries, or specific vulnerabilities associated with the chosen platform.
2. Web server configuration and software
This step involves a thorough assessment of the hosting server’s configuration and the software running on it.
It’s important to make sure that all software, including the operating system, web server (such as Apache or Nginx), and database server are up to date with the latest security patches.
The configuration should be checked for vulnerabilities such as directory traversal and to ensure that appropriate security modules are enabled.
3. Web extensions and plugins
The audit also includes an inspection of any additional functionality integrated into the site via plugins or extensions.
This includes checking for outdated or unmaintained plugins that may contain security vulnerabilities.
Each plugin or extension should be evaluated for necessity, and those that pose security risks should be removed or replaced.
4. SSL/TLS Security
The integrity and implementation of SSL/TLS protocols on the website are verified to ensure secure data transmission between the user’s browser and the website.
This includes verifying the validity and proper installation of SSL certificates and ensuring that they are up to date.
5. Data management and encryption
This part of the audit focuses on how the website manages, stores, and transmits data.
It focuses on the encryption methods used to protect sensitive information, such as user credentials and payment information.
It also includes a review of database security practices, including encryption of data at rest and secure data transfer methods.
6. Third-party integrations
Any external services or APIs integrated with the site are evaluated for potential vulnerabilities they may introduce.
This step includes evaluating the security measures of these third-party services and ensuring that any data sharing or permissions granted to them comply with established security standards.
7. Information processing and handling
The final step in this part of the audit is to review how sensitive information is processed and handled on the website.
This includes ensuring compliance with security standards and regulations, such as GDPR for personal data, and examining the website’s practices for collecting, storing, accessing, and sharing information both internally and with third parties.
8. Vulnerability scanning
This is the process of using automated tools to scan a Website for known security vulnerabilities. These tools perform scans to detect issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure server configurations, outdated software components, and other common vulnerabilities.
9. Penetration testing
Penetration testing, also called pen testing, involves simulating cyberattacks by security professionals to understand how a hacker might exploit vulnerabilities.
These pen testers use the same techniques as real attackers, but do so ethically and legally to assess security vulnerabilities.
The primary goal is to identify vulnerabilities before actual attackers do. This includes testing for issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), insecure server configurations, and authentication weaknesses.
Pen testers also evaluate the effectiveness of existing security policies and procedures. They test how well these policies hold up against attempted breaches.
Penetration testing can be manual or automated.
10. Code review
A web security audit involves systematic examination of the website’s source code to identify security vulnerabilities, coding errors, or deviations from best coding practices.
The code review process is essential for ensuring the security and reliability of a website.
11. Site settings and user permissions
Audit user accounts and permissions, as well as website settings, should be on your website security checklist, too.
It is crucial to protect against unauthorized access and potential security breaches. This review ensures compliance with the principle of least privilege, where users are granted only the access required for their roles, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and insider threats.
Regular auditing of user accounts helps identify and remediate redundant or obsolete accounts that could otherwise become security liabilities.
In addition, auditing website settings is essential for detecting configuration errors that could lead to vulnerabilities, improving overall security, and maintaining website integrity.
12. Performance and reliability testing
Performance and reliability testing is an important aspect of maintaining a website, focusing on its capacity to handle high traffic and maintain website performance under various conditions.
Although not a direct part of security audits, this testing is crucial for assessing a site’s resilience against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. By identifying how much load a website can handle before performance degradation, it helps in pinpointing vulnerabilities and planning for capacity enhancements.
This testing indirectly enhances security by preparing the site to handle potential traffic spikes and ensuring consistent performance and reliability, which are key to a positive user experience and overall site stability.
13. Reporting and remediation
After the audit, a detailed report should be prepared highlighting the vulnerabilities found, their severity, and recommendations for remediation.
This step typically includes prioritizing vulnerabilities to ensure they are addressed effectively.
14. Regular updates and monitoring
Security is not a one-time effort.
Regular updates and continuous monitoring are essential to maintaining a secure posture against new and evolving threats.
Essential web security audit tools
Acunetix
Acunetix automatically creates a list of websites, applications, and APIs for scanning, ensuring comprehensive coverage. It can scan single page applications, script-heavy sites, and applications built with HTML5 and JavaScript, including areas that are password-protected or hard to reach.
Pros
Acunetix can detect over 7,000 vulnerabilities, including zero-days. It offers a blend of DAST + IAST scanning, minimizing false positives and pinpointing exact lines of code that need fixing. Integration into developers’ tools is also a key feature.
Cons
May not be suitable for very small businesses or individuals due to pricing.
Pricing
Based on long-term subscription agreements, varying by the number of websites or web applications scanned and the length of the contract
Burp Suite by PortSwigger
Burp Suite is a comprehensive tool for web application security testing, known for its extensive scanning and vulnerability detection capabilities.

Pros
Offers a wide range of features and is considered competitively priced. The Professional edition is ideal for individual users, while the Enterprise edition is suited for larger organizations.
Cons
Some users might find the interface complex, and the learning curve can be steep for beginners.
Pricing
Burp Suite Professional is priced at $449 per user per year. The Enterprise Edition costs $9,236 per year for five concurrent scans, with additional scans at $659 each per year.
ScanRepeat
ScanRepeat is a continuous security audit tool dedicated to SaaS and ecommerce web applications which doesn’t require any code changes.
Using ScanRepeat is very easy and fast, to scan your project you need to enter a URL address of your web application. Once you’ve set up your scan project, ScanRepeat will perform security scans for the specified URL, identifying vulnerabilities, compliance issues and other potential security problems in the web application.
This process helps to detect and address security vulnerabilities proactively, ensuring that your web applications are robust and secure.
Pros
ScanRepeat stands out for its user-friendly interface, flexible scan options for multiple projects, continuous security audit capabilities, and affordable pricing, all available without the requirement of a credit card.
Cons
As the tool is designed primarily for scanning web applications, it might not be as effective or suitable for other types of cybersecurity needs or IT infrastructures.
Pricing
Pricing ranges from $9.95 for individual plans to $19 per month for commercial applications. Includes 14-day free trial.
Nessus by Tenable
Nessus is a vulnerability scanner that offers comprehensive assessments of potential vulnerabilities in web applications.

Pros
Known for its thoroughness and accuracy in vulnerability detection.
Cons
The cost can be high for small businesses or individual users.
Pricing
A one-year subscription costs $3,590, with longer-term subscriptions available at a reduced rate per year. Additional support and training options are available for an extra fee.
Intruder
Intruder is a cloud-based vulnerability scanner that helps to find weaknesses in your online systems before the hackers do1. It works by performing infrastructure security audits, cloud security reviews, and web application assessments on your systems, using a range of scanning techniques and threat intelligence.
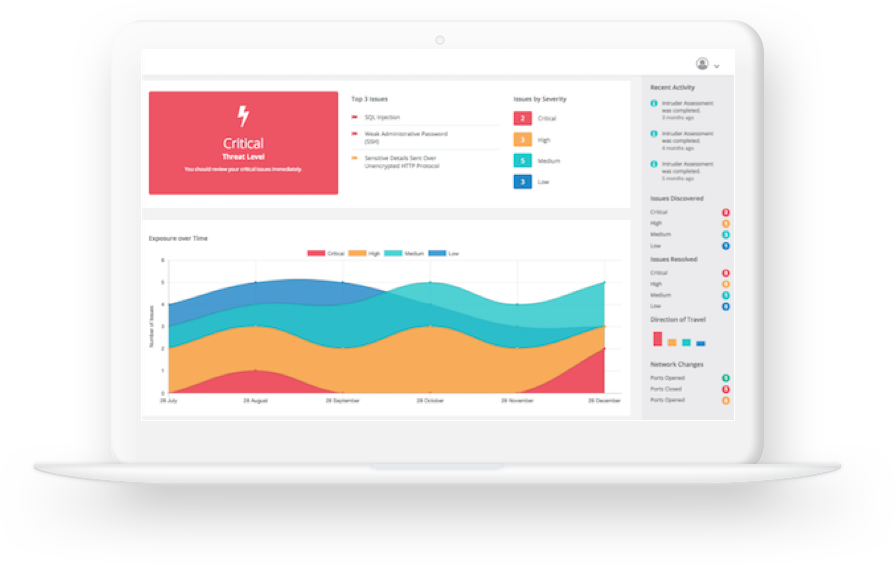
Source: Intruder
Pros
It allows you to target specific audience segments and customize your scans according to your needs and preferences.
Cons
It may not be able to detect some of the more advanced or obscure vulnerabilities that require manual testing or human intervention.
Conclusion
Keeping a website secure is a big deal. Audits help find problems before they become serious. They make sure the site is following the rules, keeping users’ information safe, and running smoothly. Regular website security audits performed with the right tools are key to keeping a website healthy in the digital world.
Related Posts
- How to Make a Calendar App: Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Build a Document Management System: Quick and Efficient Approach
- Future of Real Estate: Space as a Service Model
- 10 Key Proptech Trends in 2024: How Technology is Changing The Real Estate Industry
- How to Prepare a Successful Application Migration Project
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog post!
